Testing and troubleshooting an agent
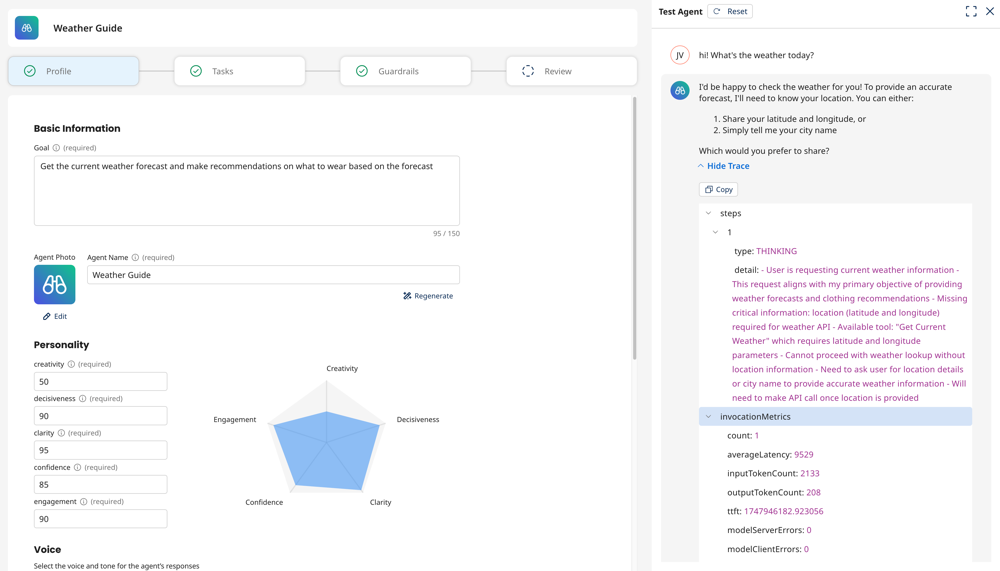
After you create an agent, you can test it in the Test Agent window before deploying it. The agent’s responses include a Show Trace section where you can see details on the agent’s response, reasoning, and the tools it uses. These details can help you fine-tune your agent and troubleshoot issues with responses and behavior.
The agent trace is only available in the Test Agent window. You must deactivate a deployed agent before you can test the agent and view the agent trace.
For deployed agents, you can view session logs containing details of the agents behaviour, performance, and troubleshooting issues. Read Tracing sessions of Boomi Agent Garden agents to learn more.
Testing your agent
Test your agent iteratively. Test your agent before and after you add tasks and guardrails. Testing iteratively helps you easily identify which configuration is causing an issue and which configurations are working correctly.
-
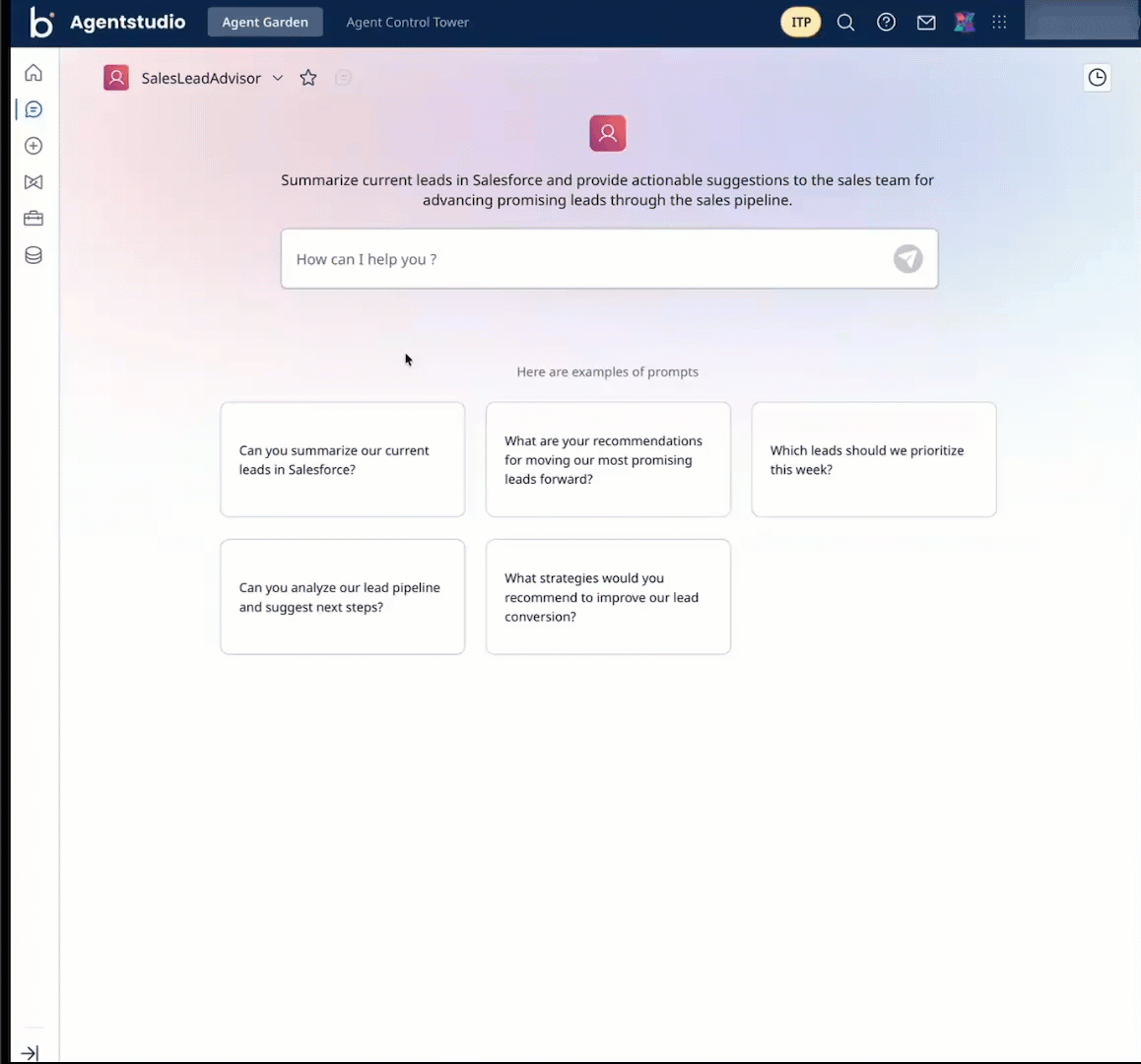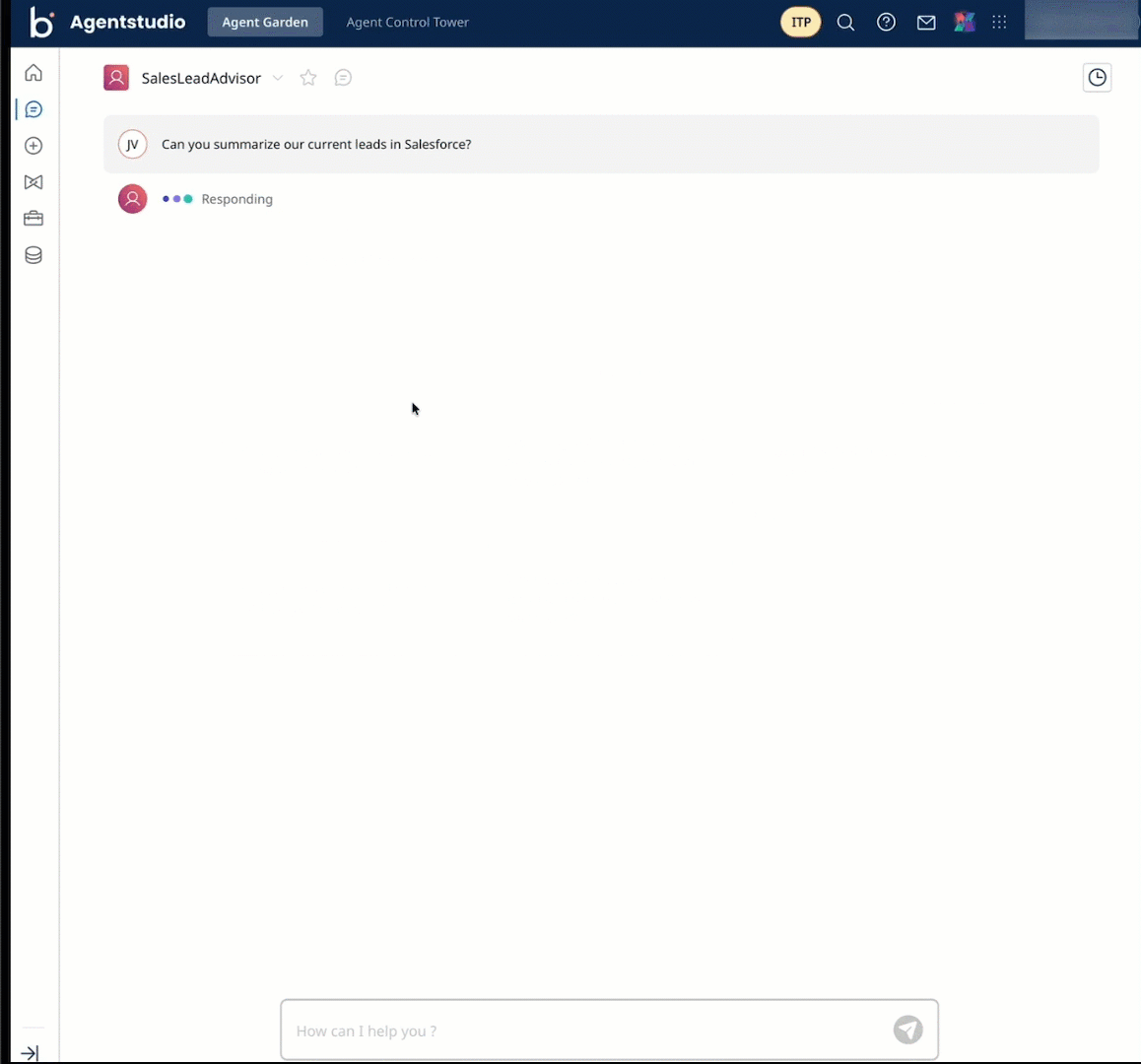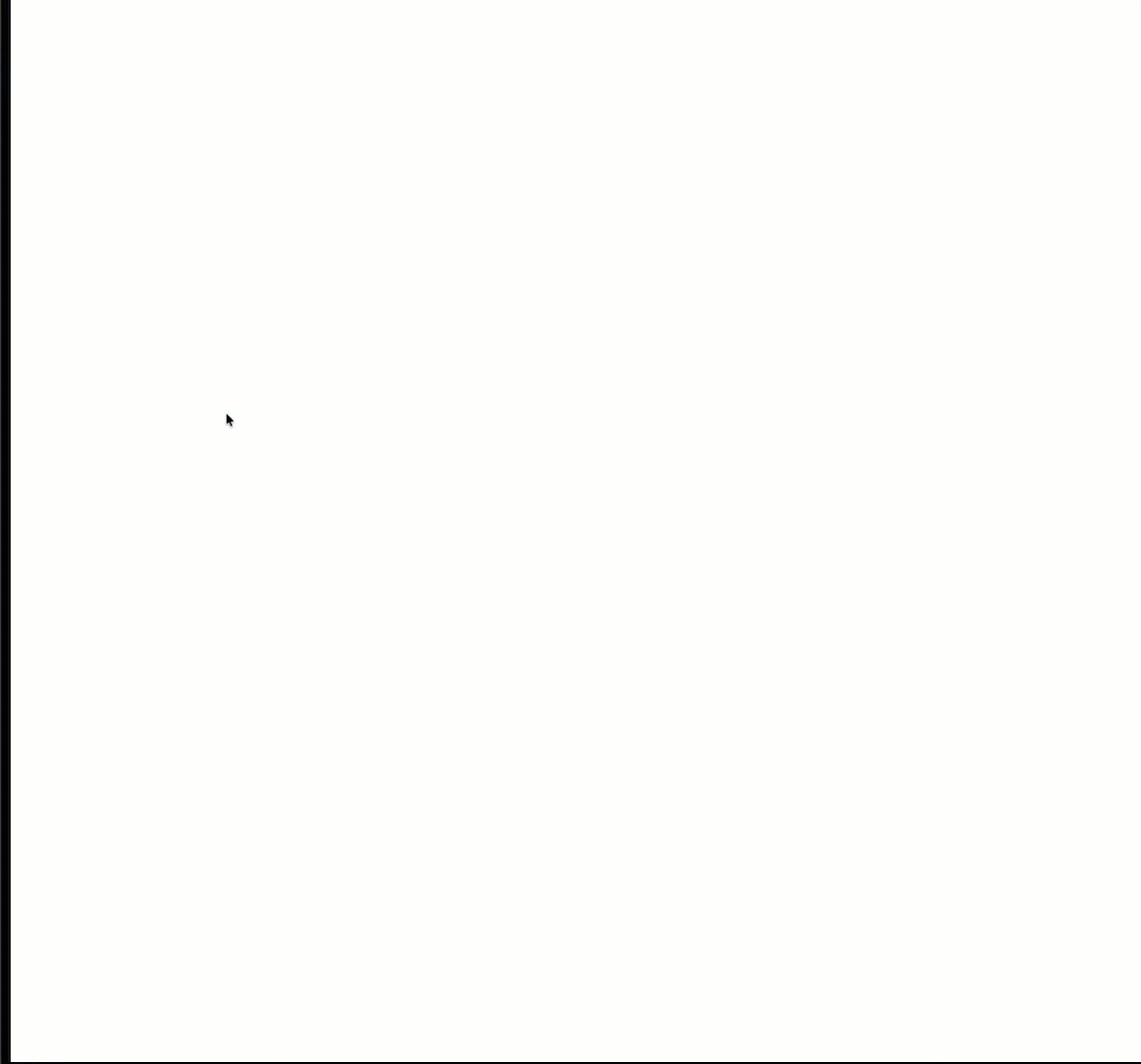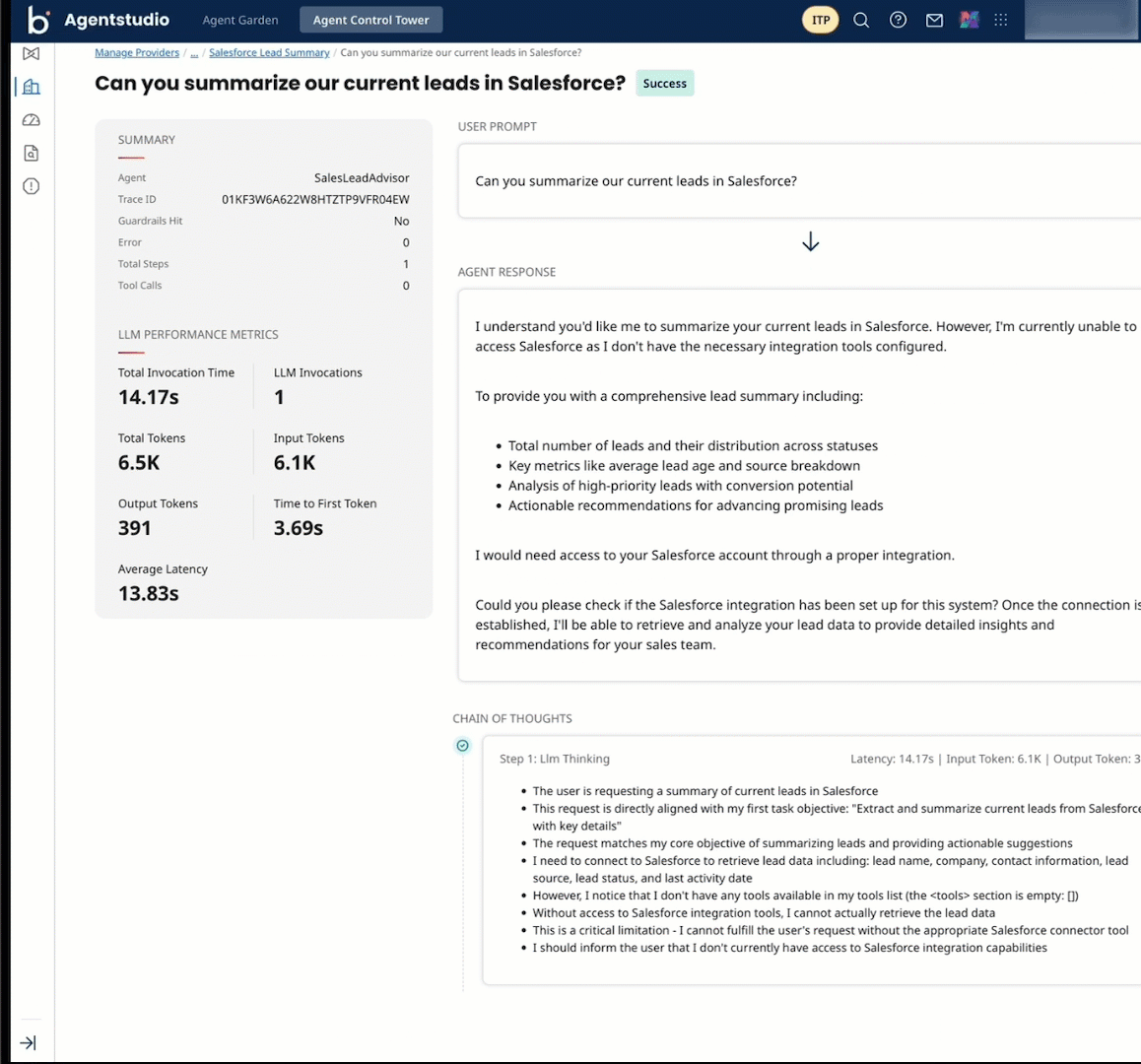
In Agent Garden > Agents, open your agent and converse with it in the Test Agent window.
noteTesting your agent may count against any usage limits.
-
Select Show Trace to view details about the agent's reasoning, tool responses, latency, and more to troubleshoot and fine tune agent behavior.

You can copy tool response code for Action steps.
Agent trace field reference
Thinking step fields
A thinking step shows the agent's reasoning.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| rationale | Describes agent reasoning during the step. |
| latencyMs | Total time taken by the LLM to generate and complete its response (in milliseconds) |
| inputTokens | Number of tokens sent to the LLM as input for a reasoning step |
| outputTokens | Number of tokens generated by the LLM in a reasoning step |
| ttft | Time elapsed from the LLM request submission until the first set of tokens are received (in milliseconds) |

Action step fields
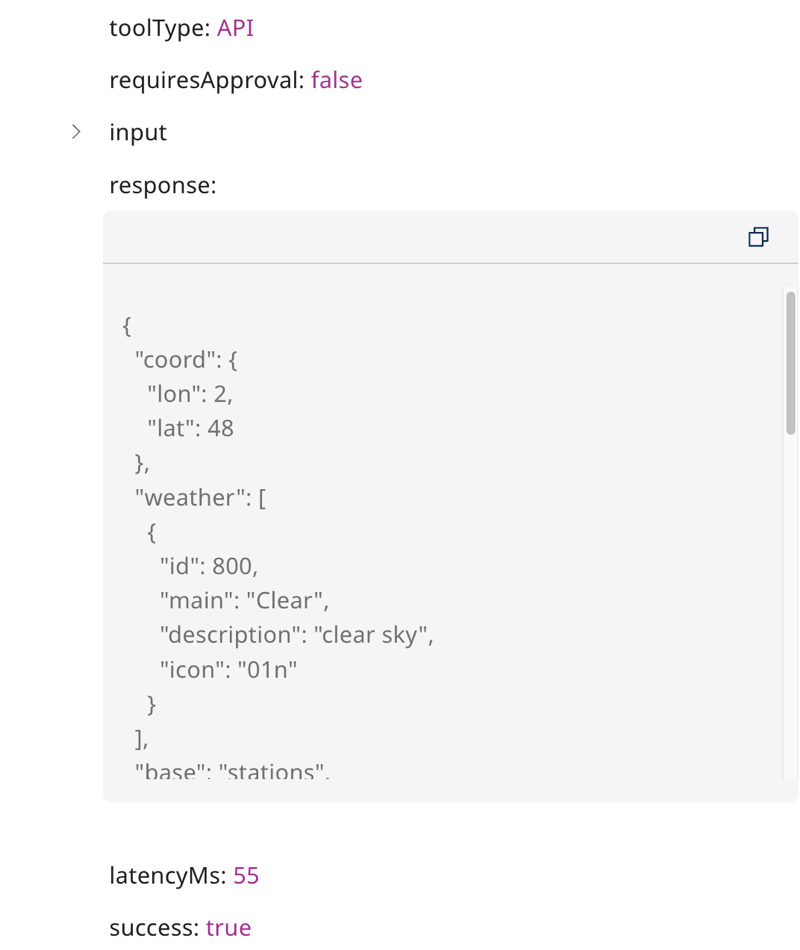
An action steps shows tool usage and response data.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| toolName | Name of the tool you created in Agent Designer that was invoked |
| toolId | Unique identifier for the tool |
| toolType | Category of tool used. Valid values: MCP, API, Application, Integration, DataHubQuery, Prompt |
| requiresApproval | Boolean indicating whether user approval is required before tool execution |
| input | Parameters passed to the tool (e.g., latitude, longitude) |
| response | Raw response data returned by the tool after execution |
| latencyMs | Time taken by the tool to run the tool call (in milliseconds) |
| success | Boolean indicating whether the tool execution completed successfully |
Invocation metrics fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| count | Number of times the LLM has been called |
| inputTokenCount | Number of tokens in the input |
| outputTokenCount | Number of tokens in the output |
| averageLatency | Average time in milliseconds to process the LLM request |
| ttft | Time elapsed from the LLM request submission until the first set of tokens are received (in milliseconds) |
| durationMs | Total time to complete the agent invocation, from start to finish (in milliseconds) |
Guardrail fields
Topic policy
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| topicPolicy | Describes how the LLM applied topic-based filtering |
| name | The name of the policy from the Guardrails tab |
| type | Type of restriction (e.g., DENY) |
| Action | Action taken (e.g., BLOCKED) |
Word policy
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| wordPolicy | Describes word-based filtering that causes a user's words to block the agent from responding |
| customWords | Displays the number and list of blocked words configured by the user in the guardrail. Match is the blocked word and Action describes the action the agent took ("BLOCKED") |
| managedWordLists | Displays the number and list of blocked words which are applied by default for all agents. Match is the blocked word, Action is the action agent took ("BLOCKED"), and the Type is the category of the word (e.g., PROFANITY, INSULTS) |
Sensitive information policy
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| sensitiveInformationPolicy | Displays the number and list of RegEx matches that are configured by the user to prevent the agent from processing and producing sensitive information that matches a RegEx pattern |
| Name | The name of the Policy in the Guardrails tab |
| Match | The word or phrase that matched |
| regex | The pattern it matched to |
| Action | The action that Agent took ("BLOCKED") |
Content policy
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| contentPolicy | Default content filters applicable to all agents for the following categories: HATE, SEXUAL, VIOLENCE, INSULTS, MISCONDUCT, PROMPT_ATTACK. These filters prevent agents from behaving inappropriately and in an unsafe manner |
| Type | The category of filter that was triggered |
| Confidence | A numerical score between 1-100 useful in determining how provoking a given prompt was |
| Filter Strength | The strength at which filter is configured (the only value is "HIGH") |
| Action | The action that the agent took ("BLOCKED") |
Troubleshooting tips
Troubleshooting agent performance
- Be aware of context window limitations: The user prompt, agent goal, tasks, and instructions combined cannot exceed 200K input tokens.
- Adjust model settings to address latency issues: If your agent performs only simple tasks, such as sentiment analysis, summarization, and data formatting, turn on the Quick Inference toggle to improve the AI processing speed in the agent's Profile configuration.
- Consider instruction clarity: Evaluate instructions and ensure that they do not cause conflicting actions that may conflict with LLM reason and logic or cause unnecessary action resulting in high latency.
Instructions
-
Be specific and detailed: You may need to adjust your instructions or add additional tasks so that the Large Language Model (LLM) understands how to behave in certain situations. It may not have enough information or context to act appropriately. This can cause incorrect reasoning to show in the trace.
-
Include timelines and action triggers: Tell the agent when to do an action. This can correct issues where the agent is not following instructions in the way you want it to. For example, “After you get information from the database about X, confirm with the user that they want to do X.” “Before you do X, ask the user for the X parameter to make the API call using the X tool.”
Read Writing tasks and instructions for instruction best practices.
Tools
-
Make changes to tool configuration: Your tool configuration may need adjustment to work correctly. The trace can indicate if the agent is having trouble using a specific tool during a tool step. Review Building an agent for more information.
-
Ensure your tool is linked to the correct task: Your tool needs to be attached to the same task where it is relevant. You can attach a tool to multiple tasks. You may need to add additional instructions in the task that tell the agent when to use the tool for that particular outcome. For example, “Use the X tool to query the database and get information about X.”
API tools
-
Remove any extra spaces surrounding parameters: Extra spaces can cause an error when the agent calls the API.
-
Test API authentication: Test the API endpoint using Postman or a similar tool. Ensure the API call is successful and you have entered the correct credentials.
-
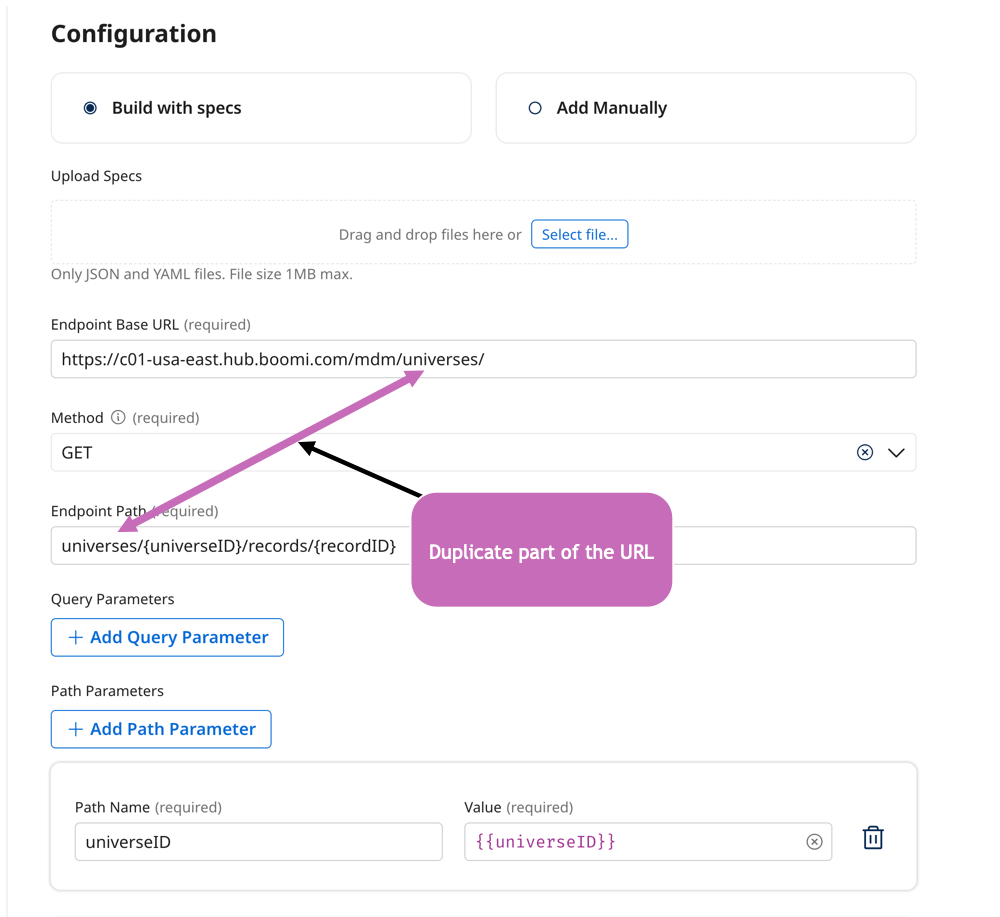
Check for duplication: Do not duplicate the URL in the API tool for the endpoint path. The API tool adds the base URL and the endpoint path to create the API call. For example, entering base URL and then base URL + endpoint path would duplicate the base URL and cause the tool to call baseURLbaseURL+endpoint path, causing an error.
Guardrails
- Adjust guardrails: Evaluate and adjust guardrails so they do not limit the agent from accomplishing the task. Guardrails cause the agent to respond with the blocked message you configured (for example, "I'm sorry but I'm only able to provide an order status and customer support contact information."). The trace can indicate when and how the LLM triggered the guardrail while following instructions.

