OP AI LLM Intelligence - Partner operation
OP AI LLM Intelligence — Partner operations provide powerful capabilities for text processing and conversational AI. They can generate embeddings for input text—producing vector representations useful for tasks like similarity search and semantic analysis—and support dynamic chat interactions by handling input within a conversation flow. Additionally, these operations can generate responses based on user input, system prompts, and specified settings. The connector also offers a reporting feature to check the current version, ensuring users have up-to-date information.
Error codes
The error codes below help identify and troubleshoot various issues that may arise during the operation of the database connector. Each code is grouped by category, making it easier to understand the type of issue and take appropriate action.
- Configuration Errors (E1##): Codes in this category indicate issues related to the setup and configuration of the connector, such as incorrect connection parameters.
- Payload Errors (E2##): These codes capture errors in the format or content of input data, including syntax and semantic validation issues.
- General Connection Errors (E3##): Codes representing connection issues, including network timeouts, data transmission errors, or interruptions during operations.
- Specific Connection Errors (E4##): Reserved for errors specific to connection types or protocols (currently no codes assigned).
- Business Validation Errors (E5##): Reserved for errors that arise from business logic validation requirements (currently no codes assigned).
- Unknown Errors (E9##): General fallback category for unhandled or unexpected issues that don’t align with other error types.
| Error Code | Name | Description | Investigation & Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1## Configuration Errors | |||
| E101 | CONNECTION_CONFIGURATION_ERROR | An error in the configuration for establishing a connection. | Verify all connection parameters (host, port, credentials, etc.). Check for typos and ensure the database is reachable. Test connectivity using a tool (e.g., telnet, ping). |
| E102 | OPERATION_CONFIGURATION_ERROR | An issue with configuring the connector's operation parameters. | Review connector-specific settings (e.g., operation type, payload mappings). Refer to the documentation to ensure the parameters are valid. |
| E2## Payload Errors | |||
| E201 | INPUT_DOCUMENT_FORMAT | A syntax error in the input request document. | Validate the input against the required format (e.g., JSON, XML, or plain text). |
| E202 | VALIDATION_ERROR | A semantic error in the input request, such as invalid data types or required fields missing. | Ensure the correct path is provided if applicable. Validate input for correctness (e.g., proper URL for extract operation). |
| E3## General Connection Errors | |||
| E301 | CONNECTION_TIMEOUT | The connection attempt timed out, potentially due to network issues or an unresponsive server. | Check the network connectivity and API status. Increase the timeout setting if necessary. |
| E302 | IOEXCEPTION | An IOException was thrown, indicating an issue with data transmission or I/O operations. | Inspect network logs for dropped packets. Check if intermediate firewalls or proxies are blocking the communication. |
| E303 | INTERRUPTED | The connection or operation was interrupted, potentially due to a thread interruption. | Verify thread stability and ensure no unexpected cancellations in the process logic. Review logs for details of the interruption cause. |
| E4## Specific Connection Errors | |||
| E5## Business Validation Errors | |||
| E9## Unknown Errors | |||
| E999 | UNKNOWN | An unhandled or unknown error occurred, serving as a general fallback for uncategorised exceptions. | Review error logs for details. |
Embeddings operation
The Embeddings operation generates vector representations (embeddings) for input text, capturing semantic meaning for applications like similarity search, clustering, and classification. The output is a JSON object containing the embedding vector, along with metadata like input token usage. You can configure this operation using the following parameters:
- Follow Redirects: A string specifying how redirects are handled.
- Input Type: A value indicating what format the input is expected to be in.
- Model: An optional string that overrides the default LLM model defined in the connection.
- Advanced Settings: If this parameter is set to true then you will be able to set query parameters and request headers.
Text to speech (TTS) operation
The text-to-speech operation converts text into natural-sounding speech audio using
various voice models. This operation processes text input and generates high-quality
audio output in multiple formats. The output includes the generated audio data
(base64 encoded), along with metadata related to the synthesis process. You can
configure this operation using the following parameters:
-
Follow Redirects: A string specifying how redirects are handled
-
Input Type: A value indicating what format the input is expected to be in
-
Model: An optional string that overrides the default LLM model defined in
the connection -
Voice: Voice to use for speech synthesis (e.g., alloy, echo, fable for OpenAI)
-
Audio Format: Audio format for the output (mp3, wav, ogg)
-
Advanced Settings: If this parameter is set to true then you will be able to set
query parameters and request headers
Image generation operation
The image generation operation creates images from text descriptions using AI models
like DALL-E or Imagen. This operation processes text prompts and generates visual
content based on the description provided. The output includes the generated image
data (base64 encoded), along with metadata related to the generation process. You
can configure this operation using the following parameters:
-
Follow Redirects: A string specifying how redirects are handled
-
Input Type: A value indicating what format the input is expected to be in
-
Model: An optional string that overrides the default LLM model defined in
the connection -
Image Size: Output dimensions for the generated image
-
Image Quality: Quality level for image generation
-
Image Style: Style for image generation
-
Image Count: Number of images to generate
-
Advanced Settings: If this parameter is set to true then you will be able to set
query parameters and request headers.
Chat operation
The Chat operation allows you to engage in conversational AI by sending user input within a dialogue context. This operation processes messages using system prompts and user-defined settings, generating dynamic responses based on input. The output includes the generated response content, any metadata related to the conversation flow, and tracked properties like input and output tokens. You can configure this operation using the following parameters:
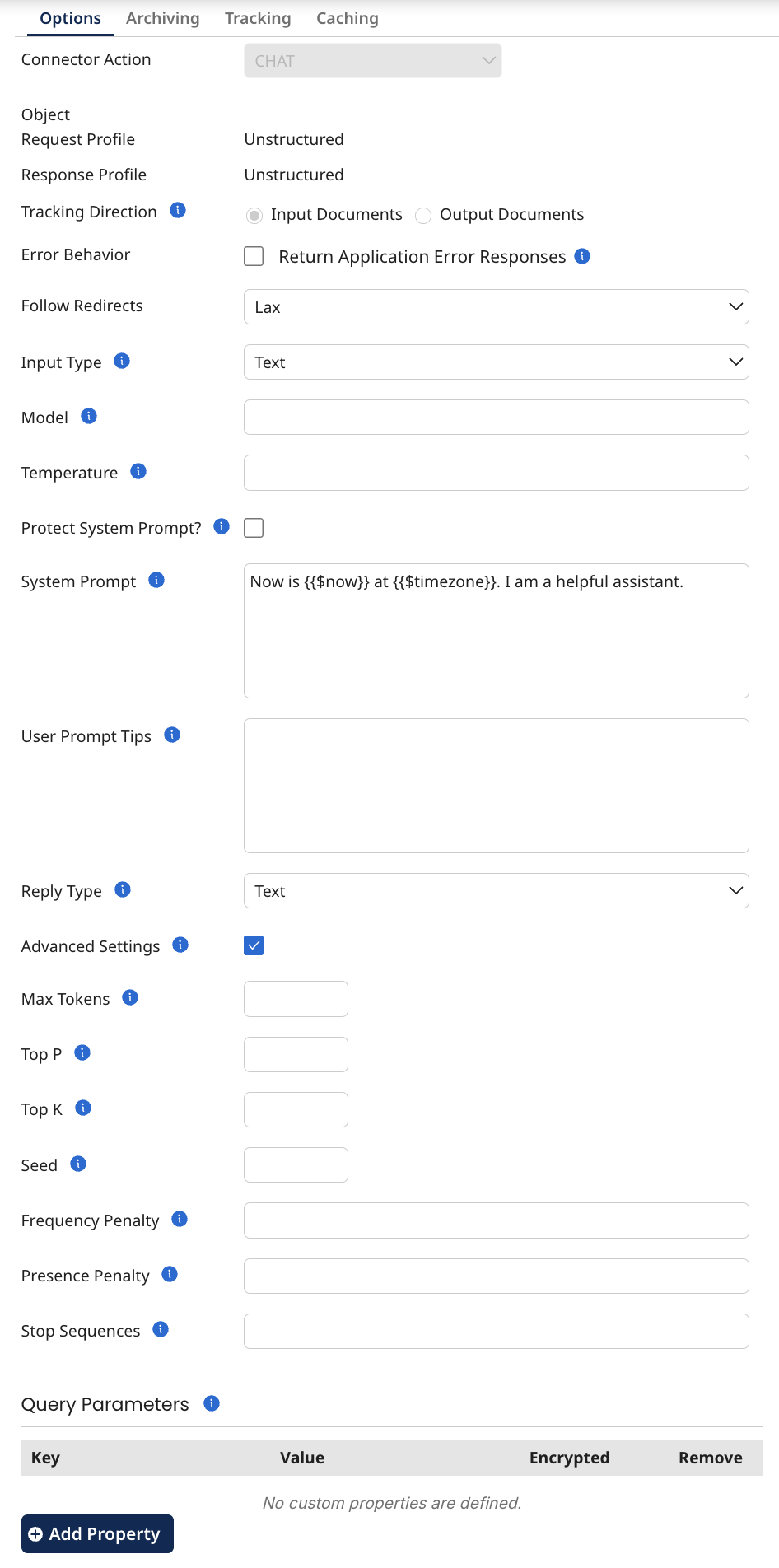
- Follow Redirects: A string specifying how redirects are handled.
- Input Type: A value indicating what format the input is expected to be in.
- Model: An optional string that overrides the default LLM model defined in the connection.
- Temperature: An optional string that controls how “creative” or “random” the answers from a model can be. A low temperature, like 0.2, makes the model safer, and more predictable words. A high temperature, like 0.8, makes the model take more risks and pick fewer common words, leading to more surprising or creative answers. (Mandatory for some models)
- Protect System Prompt?: Protects the system prompts within the process.
- System Prompt: An optional string that provides the model with specific instructions or context before it starts generating text.
- User Prompt Tips: An optional string that guides the AI on how to communicate with you effectively, such as preferred tone, response style.
- Tool Configuration: A drop-down list with the choice of how you want to
implement tools in your request. (None, Single Tool (JSON Response), Multiple
Tools) - Reply Type: A drop-down list with the choices of the response output. (Content,
Message List, Message Single) - Reply Schema: A string that defines the JSON schema that the reply should comply with. It should contain
titleanddescriptionin the specification for the model to understand better how to build that expected format. The title will be used as the tool/function name, while the description will be the tool/function description object (Only visible when the Tool Configuration is Single Tool (JSON Response)). - Tool Choice: A string that determines which specific tool or capability the model uses to fulfil a request.
- Tools: Key-value pairs representing tool functions that the model can call. The
keyrepresents the tool name and the value represents the expected json
schema for calling that tool. The json schema should containdescription(tool
description) for the model to understand better how to use that tool. (Only
visible when Tool Configuration is set to Multiple Tools) - Enable Parallel Tools: A boolean to enable parallel tool execution for multi-tool
scenarios. (Only visible when Tool Configuration is set to Multiple Tools) - Enable Conversation History: A boolean to maintain conversation context across multiple operations within the same process execution.
- Conversation ID: A string that is an unique identifier for this conversation when
conversation history is enabled. - Conversation Expiration (Minutes): An integer that represents the amount of
minutes the conversation history is kept in the cache. (default: 5 minutes) - Missing Tool Policy: A drop-down list with the values of Wait (pauses execution
until missing tool results are provided) or Discard Tool Call (removes unmatched
tool calls and continues processing). - Enable Audio Output: A boolean that enables audio response generation
(supported by some models like gpt-4o-audio-preview) - End Session: A boolean that decides whether to end the session after this
interaction. (Only applicable to Bedrock Agent) - Session ID: An optional string which represents the session ID for maintaining
conversation context. If not provided, a new UUID will be generated. (Only
applicable to Bedrock Agent) - Session Attributes: Key-value pairs to pass as session attributes to the Bedrock
Agent. (Only applicable to Bedrock Agent) - Advanced Settings: If this parameter is set to true then you will be able to set query parameters and request headers.
- Max Tokens: Optional. The maximum number of tokens is a parameter that sets the limit on how many tokens the model can generate in its response. For example, setting the value to 50, the model will stop generating after 50 tokens. This helps control the length of the answer, making sure it doesn't get too long. Token is a piece of a word, a whole word, or even punctuation that the model uses to understand and generate text. Simple words like "cat" or "dog" typically count as one token, while longer or more complex words, especially those with multiple syllables or parts might be split into several tokens.
- Top P: Optional. Alternative to temperature. Recommended for advanced use cases only. Top P is a parameter that uses nucleus sampling to control how many tokens the model considers by adding up their chances until they reach a certain percentage, like 90%. If it is set to 0.9, the model only looks at the words that together have a 90% chance of being the next word. This helps balance between choosing common and less common words, making the answers creative but still logical.
- Top K: Optional. Alternative to temperature. Recommended for advanced use cases only. Top K (or top logprobs) is a parameter that limits how many tokens the model considers before picking one. For example, if it is set to 50, the model will only consider the top 50 most likely tokens to use next and ignore the rest. This helps the model stay focused and give more sensible answers.
- Seed: Optional. The 'seed' is an initial value used to initialize the random number generator that influences the model's output. By setting a specific seed value, you can ensure that the model produces the same output each time it is run with the same input, providing consistency and reproducibility. This is particularly useful for generating repeatable results in scenarios where you need consistent outputs for testing or comparison purposes. Will be ignored for LLMs that don't support it (e.g., Anthropic).
- Frequency Penalty: Optional. Frequency Penalty is a parameter that tells the model to avoid repeating the same words too often in its response. If you set a higher frequency penalty, the model will try to use different words instead of repeating the same ones. This helps make the text more varied and interesting. Will be ignored for LLMs that don't support it (e.g., Anthropic).
- Presence Penalty: Optional. Presence Penalty is a parameter that encourages the model to use new words that haven’t appeared in the conversation yet. If you set a higher presence penalty, the model is more likely to introduce new ideas and avoid sticking to the same topics. This helps make the conversation more diverse. Will be ignored for LLMs that don't support it (e.g., Anthropic).
- Stop Sequences: Optional. Stop Sequences is a parameter (CSV format) that tells the model when to stop generating text. You can set specific words or phrases as stop sequences, and when the model reaches one of these, it will stop responding. This is useful for ending responses at the right point or avoiding unwanted continuations.
Version
Outputs the version of the build to ensure there are no mismatches between what Boomi says is being used and what is being used.
