Microsoft Excel connector
Overview
The Microsoft Excel connector lets you read and convert Excel data into structured JSON using an annotated Excel template.
A data layout is defined by a template file, which the connector uses to process matching Excel documents.
How the connector works:
-
Profile Creation:
You provide an Excel template file that uses cell comments to tag data locations — such as the start and end of tables or specific fields. The connector reads these annotations and generates a reusable data profile. -
Data Extraction:
Once the profile is created, you can process other Excel files that match the same structure. These files don’t need annotations. The connector uses the profile to extract data and generate structured JSON output. -
Execution: A basic runtime must be installed on the local machine. This is necessary to place the template in the temporary folder. The profile must be generated with this local machine. Once the profile/workflow is generated, the Excel file can be processed using the workflow on any environment (cloud runtime or local runtime).
You can download the sample annotated Excel template here to get started.
This video provides a comprehensive overview of the Microsoft Excel Connector and demonstrates how it works with annotated Excel templates:
Supported formats
The connector supports the following Excel formats:
- .xlsx
- .xlsm
The connector does not support .xls files.
Connector setup
Follow these steps to import an Excel template and create a response profile.
Configure a Process Operation
The connector supports a single Read operation that retrieves data from Excel files using a predefined template.
- Use the Import Wizard to browse and select the Excel template file from your local runtime folder.
- The connector automatically creates a response profile based on the annotated fields in the template.
You can use a template file stored in your local runtime for importing a profile object.
Only read operations are supported in this version.
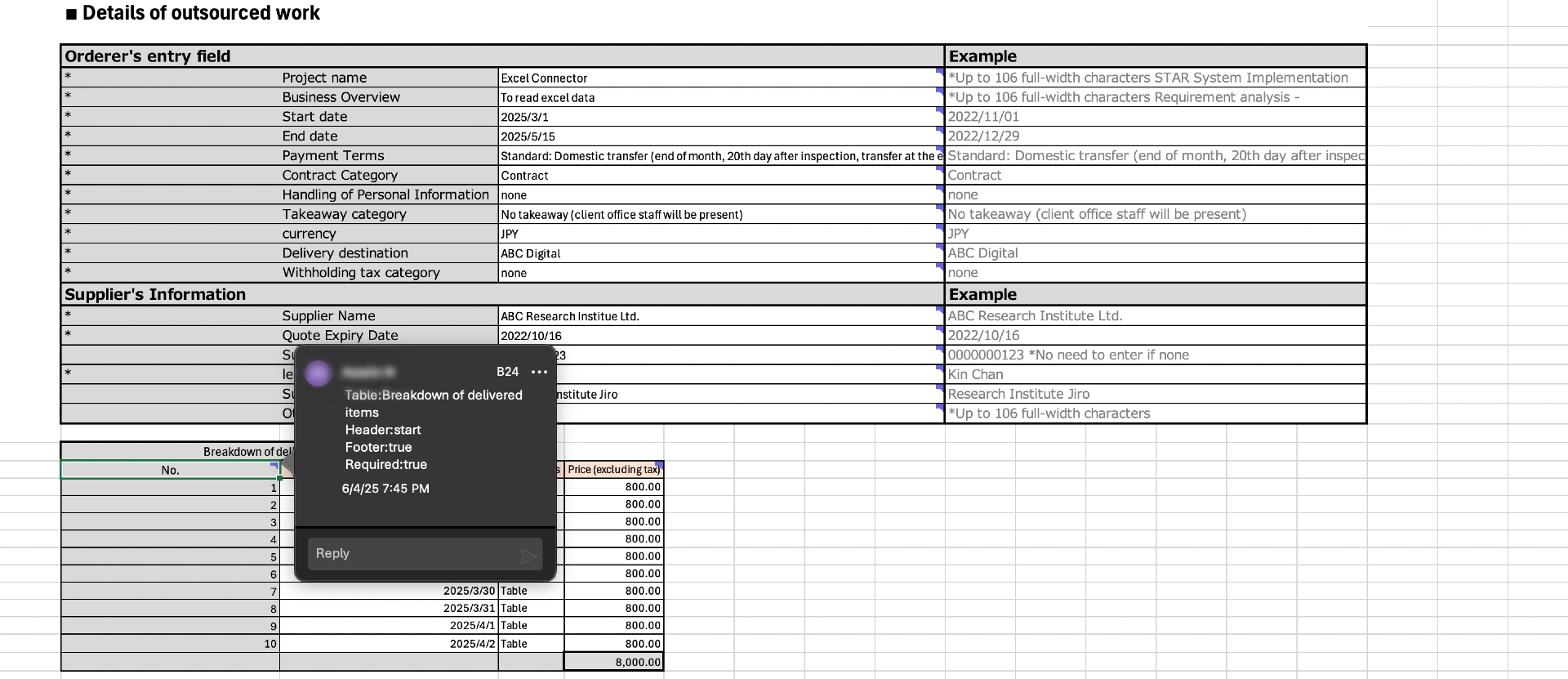
Template rules and annotations
To ensure accurate data extraction, define your Excel template using the following rules.
1. Table Identification
You annotate table start and end positions using comments in the first and last column headers.
- Table: TableName – Mandatory
- Header: start or Header: end – Mandatory
- Footer: true/false – Optional (default: false)
- Required: true/false – Optional (default: false)
You must include at least one blank line between tables to distinguish the end of one table from the start of another.
2. Data Types
- Populate the first data row in the template with correctly formatted sample values.
- If no sample is provided, the connector defaults the column type to string.
3. Tables Without Headers
If headers are missing, the system labels columns automatically (for example, Column_1, Column_2, etc.).
At least one header is required to define a table.
4. Static Fields
Static fields represent fixed cell positions, usually placed at the top of the sheet.
- Use the annotation format: Field: FieldName
- Optionally mark as required: Required: true/false (default: false)
5. Unsupported Elements
- Merged cells and macros are not supported.
- Formula results are treated as plain text values.
- The system does not evaluate or recalculate formulas.
6. Footer and Empty Rows
- The connector assumes an empty row marks the end of a table.
- If the Footer property is not defined, it defaults to
false.
7. Template and Data File Alignment
Ensure that:
- The Excel template file is available locally when designing or browsing.
- The Excel data file follows the same structure as the template for accurate processing.
Sample template file:
Actual/Data file:
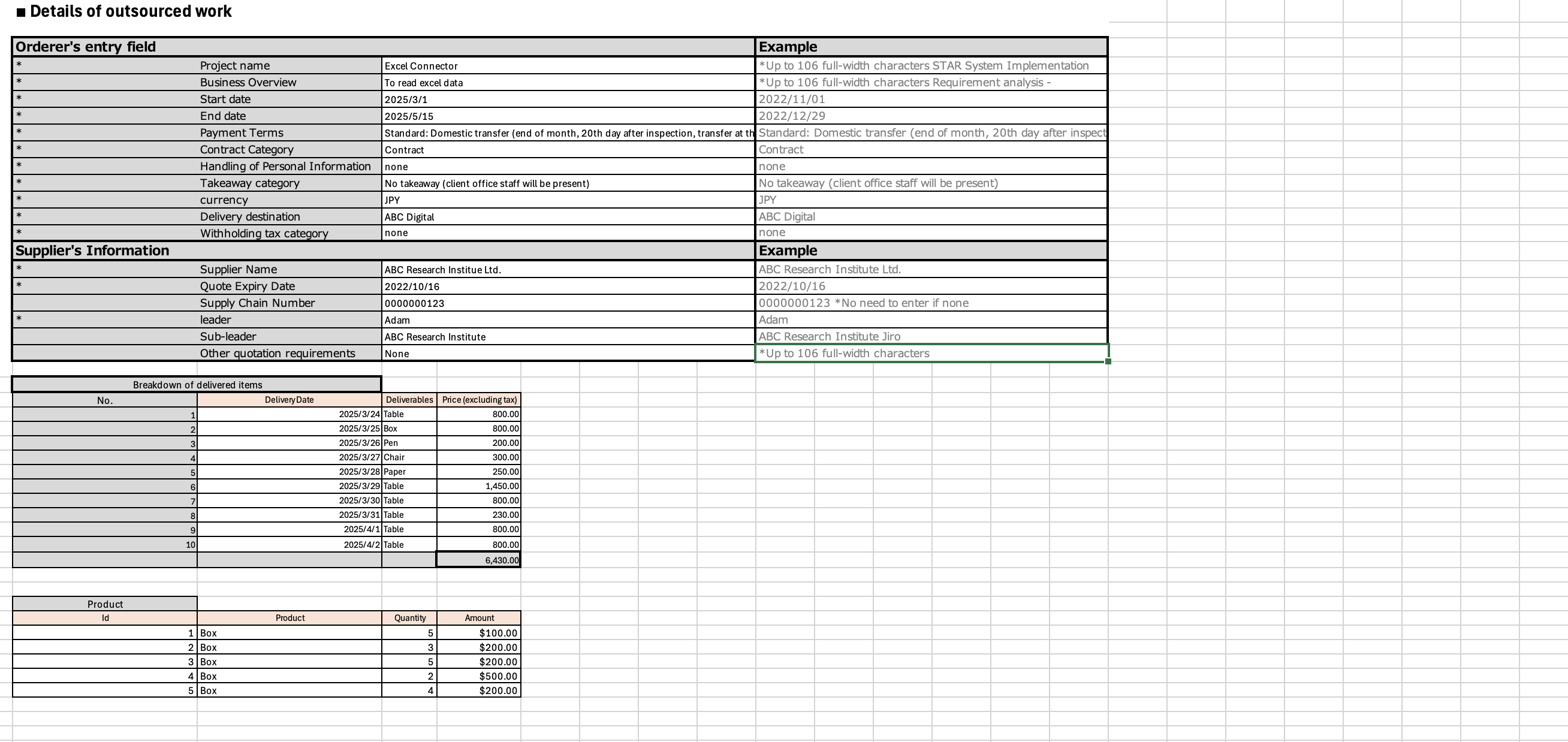
The actual Excel data file does not contain any annotations and should only include the structured data matching the template layout.
