New Source to Target experience
The new Source to Target experience is currently available only in private preview.
The "Source to Target Rivers" feature in Data Integration simplifies building robust data pipelines. It lets you extract data from a designated source and load it into a target system. This automation facilitates the detection of incoming data structures, and Data Integration generates the corresponding target tables and columns for data storage without manual intervention.
You can connect MySQL/PostgreSQL/Oracle to Snowflake/BigQuery using Data Integration Source to Target Rivers feature. Configure the source and target and establish seamless data flows between chosen platforms.
Steps to create and activate the Source to Target river
- Create a river
- Set up data source
- Set up data target
- Configure schema and Table settings
- Schedule the river
- Activate the river
Step 1: Create a river
- Navigate to the Data Integration Console.
- Click the Create Rivers → Source to Target River.
Step 2: Set up data source
- In the Source step, you can select the data source (For example, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle) from which you ingest data. You can customize the ingestion process using parameters. Data Integration provides a comprehensive list of supported connectors, letting you choose the appropriate source for your data needs.
- Creating a source connection: After selecting MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle, you must choose a connector or create a connection. If a connection exists in the Connections tab, it appears in the drop-down menu, or select Add new connection to create one.
Step 3: Select data target
-
In the Target tab, select the target (For example, Snowflake) where you load the source data. Ensure that the appropriate Snowflake instance matches the data integration requirements. This step configures the destination for the data flow, ensuring that the source data is directed to the correct Snowflake environment for further processing or analysis.
-
Creating a target connection: Select an existing Target connection or create a new one. If the Target is a cloud data warehouse, you must specify the database, schema, and target table where the data is loaded.
Data loading settings
Define a database, schema, and target table where data from your selected source lands. Data Integration automatically detects the available databases and schemas for you to choose from.
In "Snowflake" and "BigQuery", the connection form includes a Default Pre-Populated Values option. You can specify the values you want to work with, and the connection automatically remembers and uses these as the default.
Advanced settings
Data Integration provides a variety of advanced settings specific to Snowflake, letting you manage and customize data handling with precision.
-
Truncate Columns: Truncates any
VARCHARvalues that exceed the defined column length. This prevents data overflow and ensures consistency with the column definition. -
Replace Invalid UTF-8 Characters: Automatically replaces invalid UTF-8 characters with the Unicode replacement character. This ensures that invalid or corrupted characters do not interfere with data processing.
-
Add Data Integration metadata: When Data Integration metadata is turned on, additional metadata columns are added to the target table in Snowflake. These include:
River_last_update: Tracks the timestamp of the most recent update.River_river_id: Identifies the specific river used for the data load.River_run_id: Stores the unique ID of each run of the River.
You can also use custom expressions to include additional metadata fields beyond the defaults.
-
Custom File Zone:
Custom File Zone lets you specify a custom file zone for staging files before loading into Snowflake. This option helps manage file storage and properly handle large data files.
These advanced settings control data processing and storing in Snowflake, ensuring data integrity, compatibility, and enhanced metadata tracking.
Step 4: Configure schema and table settings
Extraction mode
Select the Schema type (extraction mode) that fits your requirements. Data Integration provides two types of extraction modes depending on the selected source. When using a source like an RDBMS (Relational Database Management System), you have two options for extracting data:
- Change Data Capture (CDC)
- Standard Extraction
- Change data capture
- Standard extraction
The Change data capture mode efficiently tracks and extracts the data that has changed since the last extraction, making it efficient for high-volume data sources with frequent updates.
The Data Integration Change Data Capture (CDC) extraction mode captures changes by monitoring logs or records generated by the source database, then capturing changes made to the source data. This change data is then collected, transformed, and loaded into the target database, ensuring the target is in sync with the source. For more information, refer to the Database River Modes.
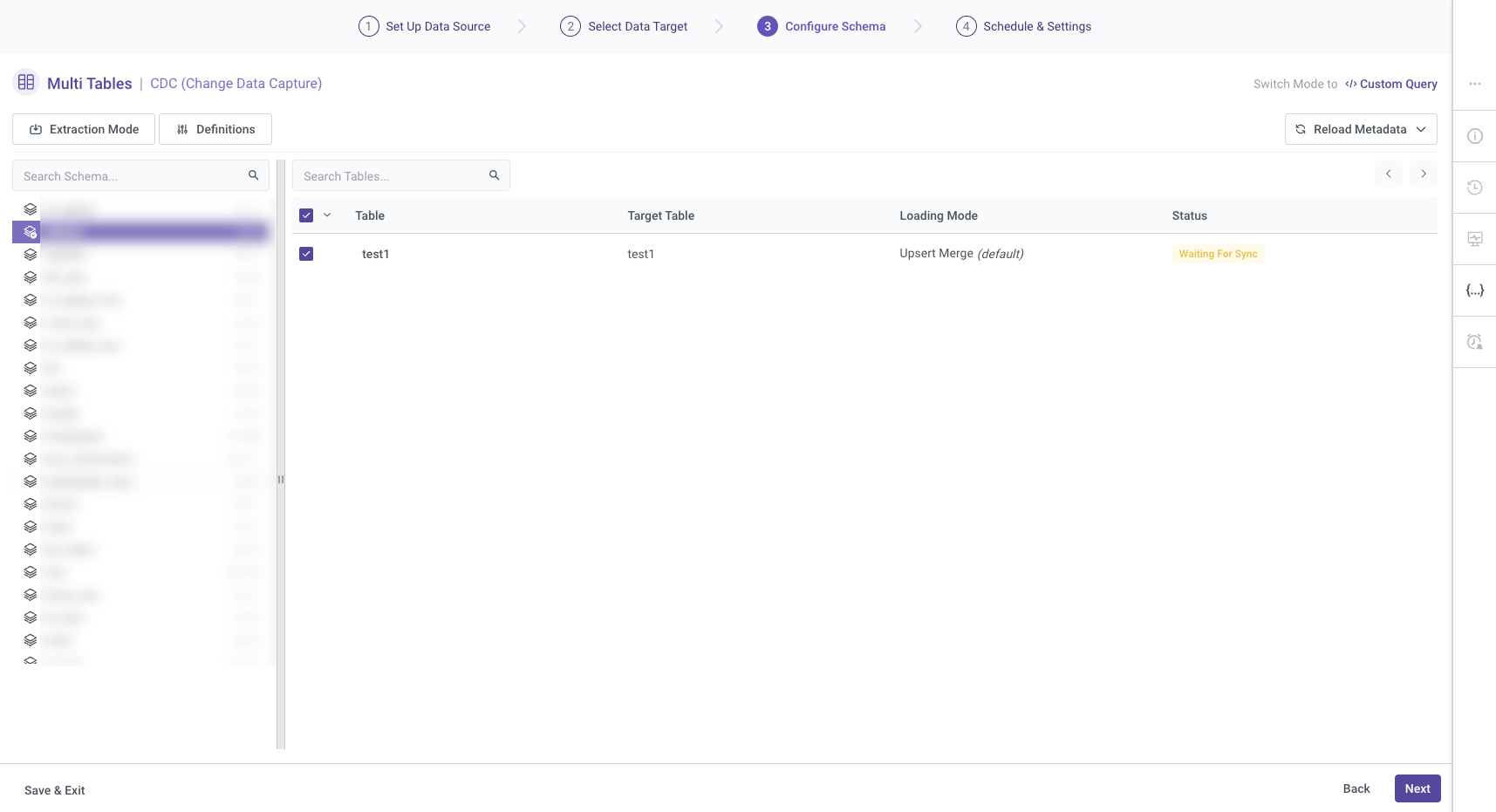
The Standard extraction mode lets you map and transform data from multiple tables into a unified schema before loading it into the destination. You establish relationships between tables to link and load the data.
The Multi-Tables River mode in Data Integration uses SQL-based queries to perform data transformations. You can configure it to run on a defined schedule or trigger it manually. For more information, refer to the Database River Modes.
After selecting the table, its name appears in the Target configuration. You can then choose the extraction method and configure it. Define specific settings to use Incremental extraction.
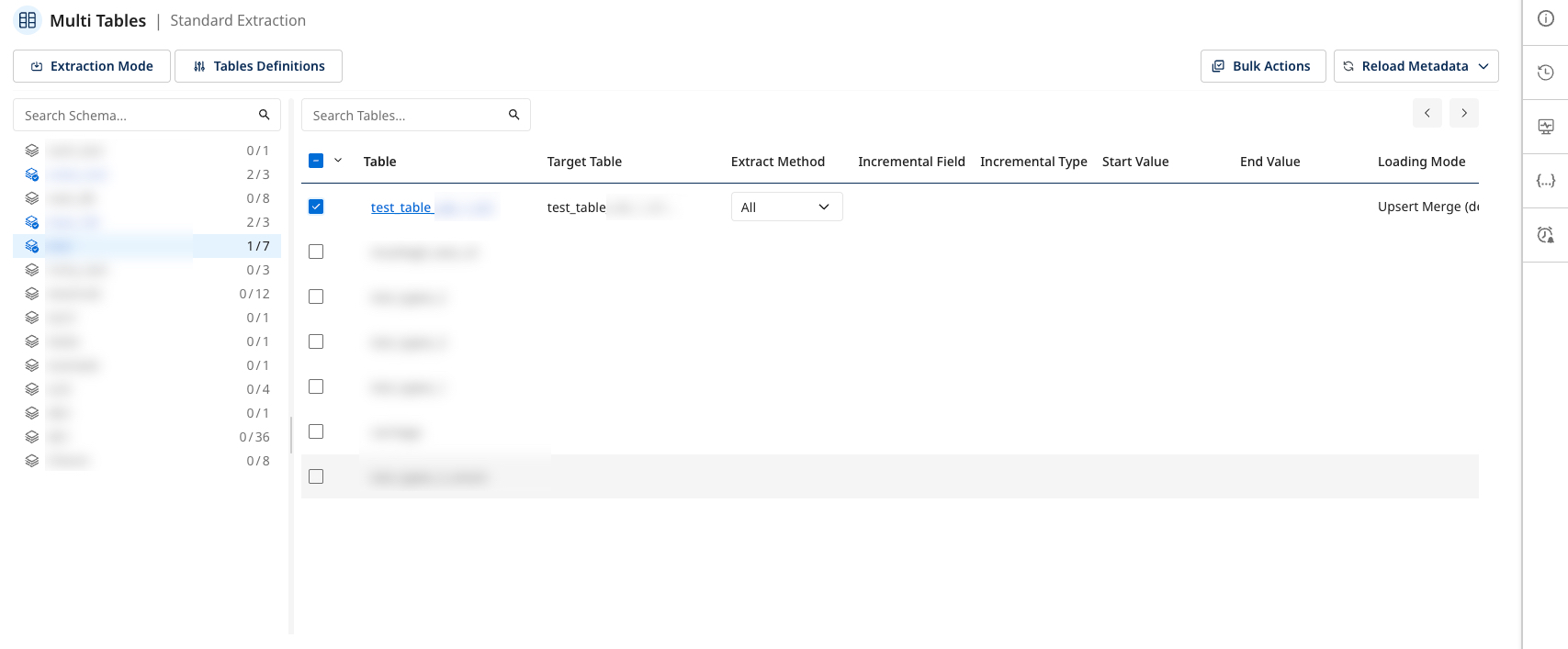
Incremental extraction (If using Standard extraction mode)
If you use the "Created_at" option in the incremental field, you must specify both a Start Date and an End Date to select the time range for data extraction. This ensures that the incremental load includes only records created during this period.
-
Start date and end date configuration:
- Start Date: Specify the beginning of the time range from which you want to pull data.
- End Date: Leave this blank if you want the data extraction to continue up to the current River execution time.
-
Automatic date updates:
- After each river run, the Start Date is automatically updated to match the previous End Date. You can set End Date to empty, letting the next run extract data from the endpoint of the previous run.
-
Time zone offset:
- Set the appropriate time zone offset to align data extraction with the local time when the River executes(if you set the "End Date" to empty).
-
Days back:
- Use the Days Back field to specify several days before the provided Start Date. This lets Data Integration to pull data from a historical point relative to the Start Date.
- The Start Date is not updated if a river run fails. To alter this behavior, navigate to More Options and select the checkbox to advance the Start Date even in the event of a failed river run.
- This is not recommended, as it may cause inconsistencies in your data extraction.
For more information on selecting time periods, refer to the Source to Target River - general overview.
Table settings
After selecting a specific table, a Settings page appears with three key options:
- Mapping
- Table Source Settings
- Table Target Settings
- Mapping
- Table source settings
- Table target settings
All columns tab
In the All Columns tab under the Mapping section, you can view the Source and Target columns and their respective data Type and Mode.
- Click the arrow icon next to a column, update the settings, and click Apply Changes to save each modification.
- You can also add a "Calculated Column" feature for advanced customizations. This feature lets you apply expressions, including mathematical and string operations, to the data from the Source. This can be useful for tailoring the output to specific business needs.
For example, use functions to concatenate fields, perform arithmetic calculations, or transform data types. For more information on using this feature, refer to the Targets.
Match key
The Match Key section lets you define the keys used to match records during data loading. Use the arrow buttons to move the relevant columns to the left table. This step is essential when using the Upsert-Merge loading mode, as at least one match key is required to identify and merge records accurately.
Cluster
The Cluster Key lets you organize data by selecting and moving the desired columns to the left table. These keys are arranged in descending order and help optimize performance when querying and managing large datasets.
The Table Source Settings section lets you define how data is extracted from the source. You can choose between Incremental or All data extraction methods, and configure Advanced Settings such as:
- Update Incremental Date Range on Failures: Determines if the date range should be updated even when an extraction fails.
- Interval Chunk Size: Defines the size of data chunks for extraction.
- Filter Expression: Enter a filter expression to control which data gets extracted.
This example is specific to Snowflake. Each Target has its own unique settings.
In the Table Target Settings, you can override the default target configuration to customize how the data is stored in the target system. Options include:
- Filter logical key duplication between files: Ensures that duplicate logical keys across files are filtered out.
- Enforce masking policy: Applies masking to sensitive data fields as per policy.
- Support escape character: Supports escape characters in data to handle special characters.
These options offer greater control over how data is handled and stored in the target.
Advanced options
Table definitions
These settings apply to all selected tables to modify schema definitions on the "Source" and "Target".
-
Advanced Source Definitions: The options vary based on the selected extraction mode.
-
Advanced Target Definitions: You can customize the loading modes depending on the target, each providing its own set of supported loading modes. For more information about loading modes, refer to the Targets topic.
Reload metadata
The Reload Metadata option is used to refresh schema metadata within Data Integration. You can choose to:
-
Reload Metadata for Selected Schema: This option refreshes the metadata for a specific schema, ensuring any recent changes are reflected.
-
Reload Metadata for All Schemas: This option updates the metadata across all schemas within Data Integration. This is useful for applying widespread updates when working with multiple schemas.
Custom query mode
Data Integration provides a Custom Query mode that lets you load data into the platform using personalized SQL queries. Use this mode when your data import requires advanced flexibility and precise control.
Key aspects of the Custom Query mode include:
-
User-defined queries: Write SQL queries to define the data to be loaded and determine the needed transformations.
-
Data sources: The Custom Query mode supports loading data from various databases and data warehouses, making it suitable for different data environments.
-
Automatic scheduling: Schedule queries to run data loads regularly or trigger them on demand, ensuring real-time access to the latest data.
Switching to Custom Query mode redirects you to the older version of Data Integration that supports this feature, and you cannot return to the previous mode. For more information on using Custom Query mode, refer to the Database River Modes.
Step 5: Schedule and settings
-
Schedule the river: The River is scheduled to run automatically by default, which is the recommended setting. However, you can customize the schedule according to your preferences.
-
Timeout settings: You can specify timeout settings for River execution. Set a timeout duration to control how long the River runs before automatically terminating. This ensures that prolonged executions do not hinder system performance.
-
Notifications: Enable notifications to stay informed about the River's execution status. Enter your email address to receive one or more notifications. To add multiple email addresses, separate them with a comma (,).
-
Additional river information: You can include any additional information relevant to the River to enhance clarity and maintain comprehensive documentation.
This topic is on an earlier UI version, but the feature remains unchanged.
Step 6: Activate river
After completing all configurations for your River, you can activate it. This step lets you verify everything works as expected.
- Click Activate to monitor the status and ensure the River initializes correctly.
Data Integration provides an additional sidebar with important options to enhance user experience.
- River Info: Access detailed information about the current river setup and configuration.
- Version history: Review the changes made to the River over time, including updates and modifications.
- Activities: Monitor and track all activities related to the River, such as data extraction and transformations.
- Variables: Manage and configure variables used within your river.
- Scheduling and notifications: Set up schedules for data runs and receive notifications based on the River's performance and status.
Managing existing rivers
Only applicable to CDC extraction mode.
Reactivation ensures that updates or modifications are applied correctly, letting the river resume processing data. You must reactivate the river to restore full feature when making changes to the river.
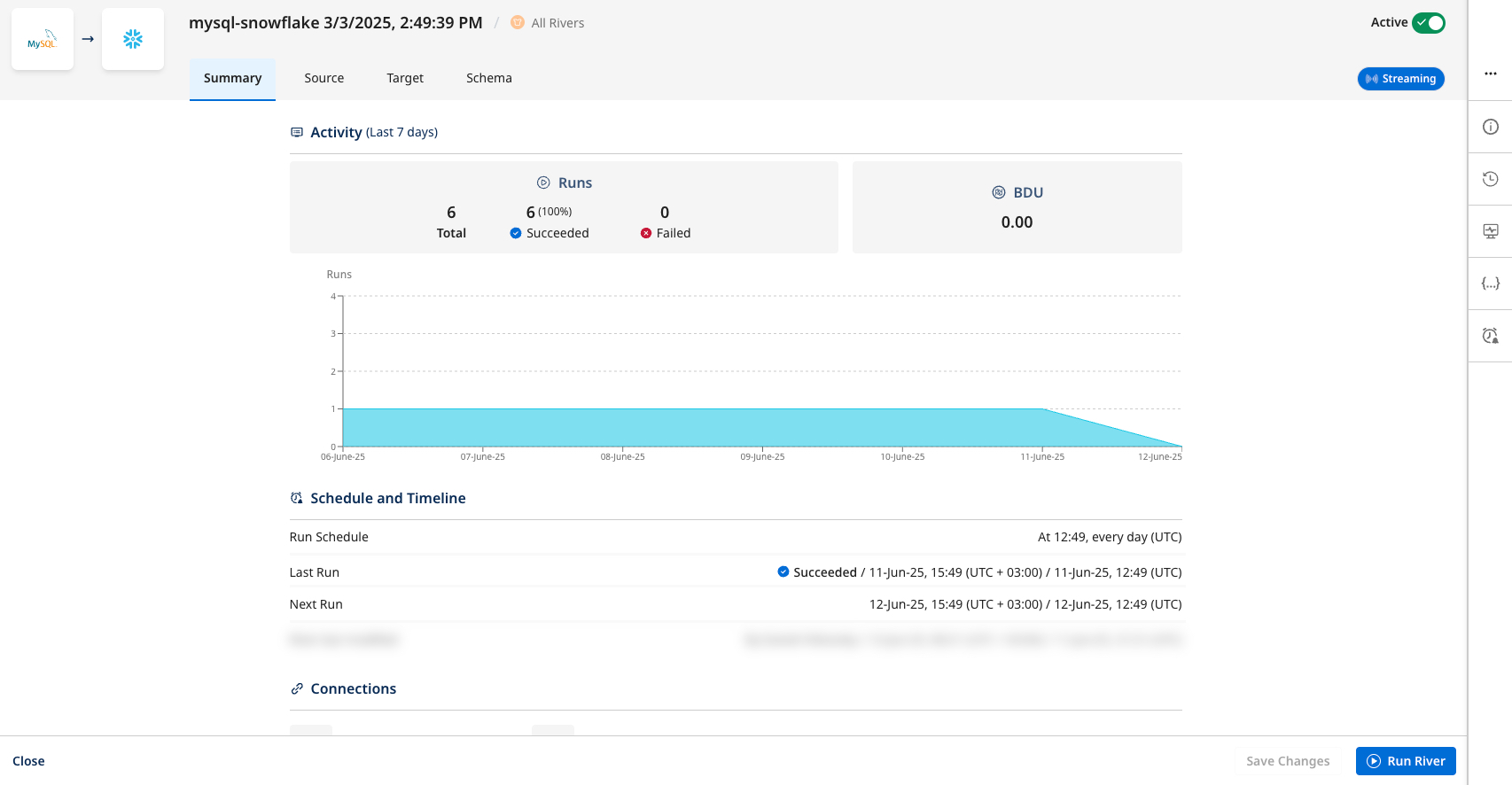
Summary page
The Summary page (first page) provides a comprehensive overview of the River’s recent activity, performance metrics, and current configuration settings, letting you quickly review its status and key operational details.
Procedure
- Navigate to the Data Integration Console.
- Click Rivers from the left-hand menu.
- Select the specific River you want to edit or review.
- The "Summary" page shows essential information about the River's current state and recent activity.
The Source, Target, and Schema tabs are identical to those used when creating a new river.
Deployments
Deploying configurations from one environment to another is supported for Rivers created using the new Source to Target experience.
The deployment process includes the following details:
-
River type and status:
- You can view the River type in the relevant column.
- You can view the current status of the "Source Environment" and the intended status of the "Target Environment".
-
Original status retention: Rivers created with the new "Source to Target experience" retain their original status when deployed to the "Target Environment". CDC Rivers are deployed with a Disabled status.
-
Existing Rivers in the target environment: If a River exists in the "Target Environment," its configuration is updated without altering its status. For example, Active Rivers remain active, and their validation state does not reset.
Recommendation: When re-validation is not required, manually reactivate the rivers in the target environment to confirm correct behavior and full integration.
