Map Function components
Map functions allow transformation logic to be applied to individual field values as they are being mapped. For example, you may want to convert a character to uppercase, to a Japanese character, change the format of a date, or look up a value in a database.
There are two main types of functions:
-
Standard — Standard functions perform a single step such as converting a value to uppercase, converting to Japanese characters, or performing mathematical operations. See the full list of standard functions below.
-
User-Defined — User-defined functions enable sophisticated transformations by allowing you to link multiple standard functions steps together in a defined sequence. They are saved as standalone components and can be reused in multiple maps.
Any function input can be mapped from the source data. This includes inputs like Fix to Length, String to Search, and Value to Multiply, however, these values are often static and therefore configured as default values.
You can access the Get Functions Require Input option in the Map Function Config dialog by clicking the three dots in the Function column. This option is selected by default, requiring input data for Get functions to run. When cleared, you can pass empty or partial source values, and the Get functions will still run.
Map function caching
When you add a standard function to a Map step, you can enable map function caching in that step. Map function caching allows you to avoid re-executing expensive and time-consuming operations such as database or connector calls. If map caching is enabled for a function, every time the Map step’s function executes it records the inputs for the function and the returned output. On a subsequent call if the input is the same, the previously returned output is returned rather than re-executing the map function.
These options control how long the cached results are held, that is, how frequently the map function cache is cleared. They appear in the Configure Defaults dialog.
-
None (the default) — Map function caching is not used.
-
By Document — The map function cache’s values are cleared after each document is processed.
-
By Map — The map function cache is not cleared. Its values are available for all documents processed by the map.
Map function caching differs from document caching in two ways: you cannot select documents from other sources and put them into a map function cache, and a map function cache cannot be used elsewhere in the process. If you want to do either of those things, use a Document Cache component instead.
Map function execution order
Map Function Ordering can be enabled for a map. This lets you control the order in which map functions are applied.
-
Map Function Ordering is off by default. All map functions are applied to one input document at a time. The order in which functions are applied is non-deterministic and may vary from one process execution to the next or even from one document to the next.
-
If Map Function Ordering is on, individual map functions are applied one at a time in the configured order to all input documents in succession. Map function ordering is useful, for example, when you need to store a value in a process property and use a different function to extract that value. Map function ordering may also be useful with specialized summing functions using process properties or external systems. You should only enable Map Function Ordering if you need it, though, because it impacts performance.
The Map Function Ordering dialog is used to enable and configure map function ordering.
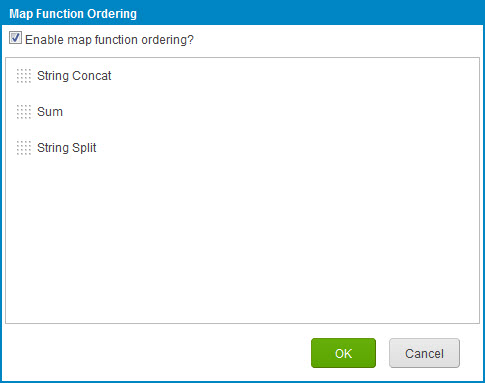
To open the dialog click
Order function executions in the Functions column.
Map Function copy and pasting
The Map Functions that are defined within your Map component or the individual Map Function steps that make up a user-defined Function can be copied. When a Map function or a Map Function step is copied, it can be pasted either into the same Map or Map Function component or another one in the same account or any account that you have access to.
Standard functions
Connector functions
| Name | Parameters/Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connector Call | - Connector - Connection - Operation - Inputs: One for each filter/input parameter required by the operation -Outputs: One for each value from the response message to be returned | Perform a call out to any application connector. Typically used to perform cross-reference lookups or obtain supplemental data. |
The Runtime Map Extension API object and Environment Map Extension API object do not support this feature.
Custom scripting functions
Custom scripting functions let you perform sophisticated field-level transformations and conditional logic. You can configure a custom scripting function in two ways:
- Insert an inline script for one-time use.
- Reference a Map Scripting component that is available for reuse.
| Name | Parameters/Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Scripting (inline) | - Use Inline Script - Language -Script to Execute -Inputs - Outputs | Insert inline custom scripting to perform field-level transformations and conditional logic using JavaScript, Groovy v2.4, or Groovy v1.5 syntax. You can add a custom scripting map function step directly to a map or within a user-defined function. Putting custom scripting steps (even simple ones) within a user-defined function allows you to reuse them. This also allows you to remove the scripting step from a map temporarily without having to recreate the entire step later. Adding input and output parameters declares them as variables to use in your script. Blank/omitted/null inputs and outputs are treated as empty strings (""). |
| Scripting (component) | - Use Scripting Component - Map Script | Reference a Map Scripting component to perform field-level transformations and conditional logic. You can choose an existing Map Scripting component or create a new one. |
For more information about custom scripting functions, refer to:
Date functions
Date functions let you reformat a value to a specific date format.
| Name | Parameters/Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Date Format | - Date String: The date value you want to reformat - Input Mask: Source format - Output Mask: Destination format | Reformat the value by specifying a date format. You can avoid using a Date Format function by configuring the source and destination profile elements to be a Date/Time type and specifying the format. |
| Get Current Date | None | Retrieve the current system date/time. |
If you require mapping to convert date and time data types, it is important to understand that when the mapping engine parses a value configured as date and time, it converts it to a special internal date format that looks like this: yyyyMMdd HHmmss.SSS. For more information, refer to Time Zone Offsets.
You can choose from the following date formats in a date function:
| Format | Example |
|---|---|
| MMddyyyy | 04242025 |
| MM/dd/yyyy | 04/24/2025 |
| MM-dd-yyyy | 04-24-2025 |
| MMddyy | 042425 |
| yyyyMMdd HHmmss | 20250424 121547 |
| yyyyMMdd HHmmss.SSS | 20250424 121547.205 |
| yyyy-MM-dd | 2025-04-24 |
| yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss | 2025-04-24T12:15:47 |
| yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssZ | 2025-04-24T12:15:47Z |
| yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z' | 2025-04-24T12:15:47.205Z |
Language functions
Language functions perform alphabet and character transliterations.
| Name | Parameter/Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Japanese Character Conversion | - String to Convert - Input - Convert from - Character set: Any, full-width or half-width Katakana, or Hiragana - Convert to - Character set: Full-width or half-width Katakana or Hiragana - Output - Result of converted character | Converts the input string between supported Japanese character sets, Katakana and Hiragana. For more information, refer to Understanding Japanese Character Conversion |
Lookup functions
| Name | Parameters/Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Lookup | - Connection: Database (Legacy) Connection to query. - Type: Standard or Stored Procedure. - SQL Statement to Execute: Query statement to execute. - Inputs: One for each dynamic parameter in the query. - Outputs: One for each column in the result set. | Execute a static or dynamic SELECT query against a database. Typically used to perform cross-reference lookups or obtain supplemental data. Note: The Runtime Map Extension object and Environmental Map Extension object of the AtomSphere API do not support this function. |
| Cross Reference Lookup | - Cross Reference Table: Used to select a cross reference component. - Lookup References: Cross reference inputs from source. - Values: Cross reference outputs to destination. | Perform static cross reference translations against a specific Cross Reference Table component. |
| Document Cache Lookup | - Choose Document Cache: Document Cache component to query. - Cache Index: Document Cache component's index to use. - Outputs: Choose one or more elements from the Document Cache component's profile to be used as outputs. | Perform a dynamic lookup against a Document Cache component and retrieve particular fields from a document. If the lookup returns more than one document, you will receive an error message. |
| Simple Lookup | - Add Row: Used to add a key/value pair. - Delete Row(s): Used to delete the selected key/value pair(s). - Selection check box — Used to select one or more key/value pairs. - Key: Column for entering keys. - Value: Column for entering values. | Basically the same as the cross reference lookup, but limited to one key returning a single value. There is no component associated with this function, therefore it cannot be shared or reused. The table of key/value pairs is embedded within the function. These lookup functions can be set up in maps or in data map extensions. |
Numeric functions
To add a numeric function to a map, click the plus icon in the Functions column. In the Add a Function dialog, select Numeric for the Category and then the type of numeric function that you want to add. You can select from the following types of numeric functions:
| Name | Parameters/Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Math Absolute Value | - Value: Input | Absolute value of a number. |
| Math Add | - Value: Input - Value to Add | Add one value to another value. |
| Math Subtract | - Value: Input - Value to Subtract | Subtract one value from another value. |
| Math Multiply | - Value: Input - Value to Multiply | Multiply one value by another value. |
| Math Divide | - Value: Input - Value to Divide | Divide one value by another value. |
| Math Ceil (Ceiling) | - Value: Input | Round the value up to the nearest whole number. For example, 1.2 to 2.0. |
| Math Floor | - Value: Input | Round the value down to the nearest whole number. For example, 1.9 to 1.0. |
| Math Set Precision | - Value: Input - Number of Precision: Number of decimal places | Set the number of decimal places for the value. |
| Number Format | - Number String: Input - Input Mask: Source format - Output Mask: Destination format | Reformat the value by specifying a numeric format. You can avoid using a Number Format function by configuring the source and destination profile elements to be a Number type and specifying the format. |
| Running Total | - Value to Sum: Input | Maintains a running total of the values passed into it. The incremental total is output per destination "detail" instance. |
| Sum | - Value to Sum: Input - Reset Value: Value used to reset sum. | Calculates a sum based on a particular "Reset Value". For each unique value of the "Reset Value", a sum is calculated. The total is aggregated and output only once per destination "header" instance, per "Reset Value". For example, use the Sum function to add up a number of order line amounts and map out the order total to a header or summary field. |
| Count | - Field to Count: Input - Reset Value: Input | Works similarly to the Sum function but increments based on the presence of a static value. By default, it increments by 1 each time for each source input and output one final value. |
| Line Item Increment | - Increment Basis: The value by which to increment - Reset Value: The value at which you want the line item increment to reset | Built-in counter that automatically increments for each occurrence of a source record. The result is output per destination "detail" instance. For example, use the Line Item Increment function to output the line number for each order line. |
| Sequential Value | - Key Name: An arbitrary, unique name for the counter. - Fix to Length: The length of the sequential value to be returned. The value is padded with zeros (0's) to the specified length. - Batch Size: Number of sequential values to "reserve" in memory (default is 1). | Built-in counter that automatically increments for each occurrence of the source record. The Key Name entity stores the latest value so future process executions continue to increment by 1 from the last result. Each counter is an ever-increasing value. Counter values are stored per Runtime. If a given process is deployed to a different Runtime, the next sequential value is different. |
After you've added the function, you can enter optional default values in the Configure Defaults dialog. The following example shows the dialog for a Math Add function:
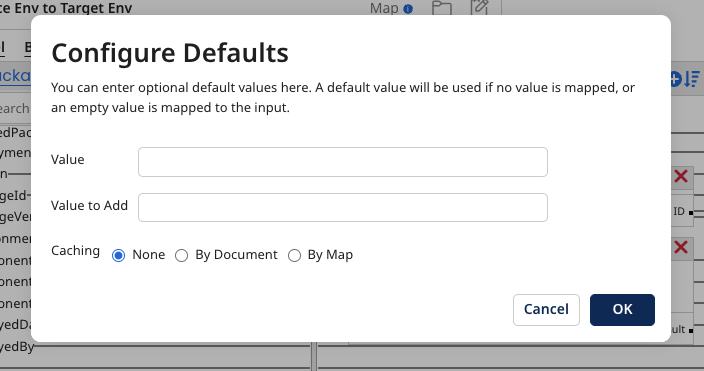
The Configure Defaults dialog varies depending on which type of numeric function you want to add to the map.
Properties functions
Properties functions are a type of custom scripting function.
| Name | Parameters/Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Get Process Property | - Property Name: Name of property - Default Value: Optional value if property is blank | Retrieve the value of a process property. |
| Set Process Property | - Property Name: Name of property - Value: Value to store in property | Set the value of a process property. |
| Get Document Property | - Property: Choose the specific document property | Retrieve the value of a document property. |
| Set Document Property | - Property: Choose the specific document property | Set the value of a document property. |
| Set Trading Partner | - Standard: Choose the EDI standard (e.g., X12, EDIFACT, HL7, etc.) - Input Type: Identifier or Control Info | Sets the trading partner for the outbound message based on trading partners in Trading Partner steps in process. |
String functions
| Name | Parameters/Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Left Character Trim | - String to Trim: Input - Fix To Length: Length of output value | Removes characters from the left side of the value |
| Right Character Trim | - String to Trim: Input - Fix To Length: Length of output value | Removes characters from the right side of the value |
| Whitespace Trim | - Original String: Input | Removes all white spaces from the beginning and the end of the string value. |
| String Append | - Original String: Input - Fix To Length: Length of output value - Char to Append | Add characters to the end of the value. |
| String Prepend | - Original String: Input - Fix To Length: Length of output value - Char to Prepend | Add characters to the beginning of the value. |
| String Concat | - Delimiter: Character between inputs - Fix to Length: Numeric length limit for characters - Inputs: Input values to concatenate in order | Concatenates string values in order |
| String Replace | - Original String: Input - String to Search: Search pattern - String to Replace | Replace a given character or string with another. This can use regular expression syntax. |
| String Remove | - Original String: Input - String to Remove: Search pattern | Remove a given character or string from the value. This can use regular expression syntax. |
| String To Lower | - Original String: Input | Converts the value to lowercase. |
| String To Upper | - Original String: Input | Converts the value to uppercase. |
| String Split | - Split By: Method to split input value - Value: Delimiter or Field Length number to split by - Outputs: Output values of the split | Splits string input value into multiple, defined output values. |
