HTTP Communication Method configuration
Overview
Use the HTTP Communication Method to configure how your process connects to an external HTTP or HTTPS endpoint. This configuration defines where your process sends requests or listens for incoming HTTP messages.
To set up HTTP as a communication method for a trading partner, you can use default settings, shared communication, or manually configure specific settings in the Edit HTTP Configuration dialog. The dialog opens from within the trading partner Communication tab when you add HTTP as a communication method or click HTTP in the Communication Method list.
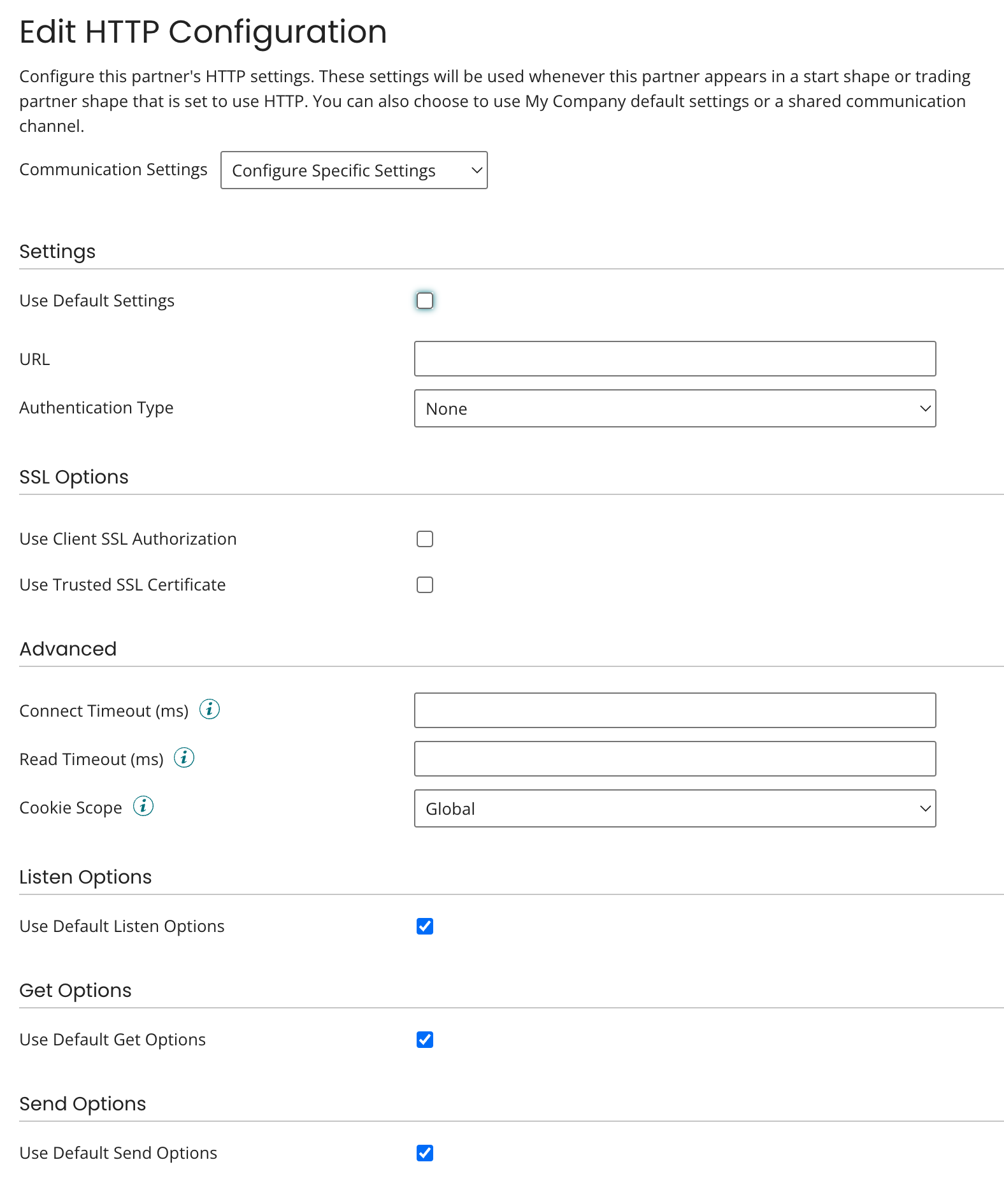
The HTTP Communication Method enables your process to send, receive, or listen for data using the HTTP or HTTPS protocol.
You can configure it in one of three modes:
-
Get – Retrieve data from an external service.
-
Send (POST, PUT, DELETE) – Send data to an external service.
-
Listen – Receive data when an external system sends a request to your runtime.
URL (Endpoint)
The URL defines the full address of the HTTP service where the process sends requests or listens for incoming messages.
For Get and Send actions, the system sends the request to the target endpoint identified by the URL.
For Listen actions, the URL defines the relative path where your runtime receives incoming requests.
| Mode | Example URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Get | https://api.tp-company.com/v1/customers | Retrieves data from the TP API |
| Send (POST) | https://api.tp-company.com/v1/orders | Sends order data to the TP API |
| Listen | /api/documents/receive | Receives incoming documents from external applications |
Authentication
Most HTTP endpoints use authentication to ensure they accept only authorized requests.
Username and Password
If the target service uses Basic Authentication, provide a valid Username and Password.
-
The process includes the credentials in the HTTP request header when sending the request.
-
The external service validates them before granting access.
Your company’s TP API or other external endpoints may require authentication to restrict access. The system rejects the request with a 401 Unauthorized or 403 Forbidden error when the credentials are invalid.
OAuth 2.0 Authentication
If your HTTP endpoint uses OAuth 2.0, configure it using an existing or new OAuth 2.0 profile.
OAuth 2.0 provides a secure way for Boomi to access external APIs without storing your username and password directly. Instead, the connector uses access tokens generated by an authorization server.
-
In the Authentication Type field, select OAuth 2.0.
-
Choose an existing OAuth 2.0 Profile, or click Create to define a new one.
-
Enter the required fields:
-
Authorization URL – URL of the authorization server.
-
Token URL – URL to exchange authorization codes for tokens.
-
Client ID – Provided by your API administrator.
-
Client Secret – Secure credential paired with the client ID.
-
Scope – Defines the level of access requested (optional).
- Click Save and test the connection.
| Field | Example Value |
|---|---|
| Authorization URL | https://auth.tp-company.com/oauth2/authorize |
| Token URL | https://auth.tp-company.com/oauth2/token |
| Client ID | boomi_tp_client |
| Client Secret | ******** |
| Scope | api.read api.write |
Use OAuth 2.0 for production integrations as it provides token-based access and securely rotates credentials without requiring process updates.
-
OAuth 2.0 is not backward compatible with OAuth 1.0 or 1.0a.
-
If your account uses custom policy files, you must edit account permissions to enable OAuth 2.0 authentication for your cloud application.
-
OAuth 2.0 settings in Boomi are extensible, allowing advanced configuration and token customization.
SSL options
SSL options control how the runtime authenticates and secures HTTPS connections using client and server certificates during SSL/TLS communication.
Use Client SSL Authorization
-
Enable this option to authenticate the client to the server using an SSL certificate.
-
Choose the Client SSL Certificate from the list of available certificates.
Use Trusted SSL Certificate
-
Enable this option to validate the server’s SSL certificate against the runtime’s trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). The runtime connects only if the server presents a valid, trusted certificate.
-
Choose the Trust SSL Server Certificate from the list of available certificates. This ensures secure connections and prevents communication with mistrusted or self-signed servers.
HTTP actions
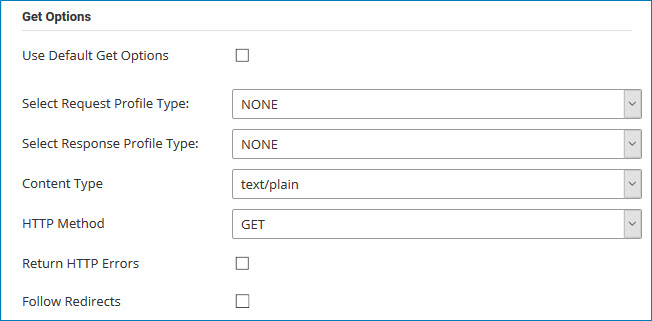
Get (Retrieve Data)
Use Get to request or fetch information from an external service.
-
The process sends an HTTP GET request to the target URL.
-
The service returns data in the response body (commonly JSON, XML, or plain text).
-
Use a Response Profile in the connector operation to parse the response format.
Example Use Case
Retrieve a list of documents from the TP API:
| Field | Example |
|---|---|
| URL | https://api.tp-company.com/v1/documents |
| Method | GET |
| Headers | Accept: application/json |
The process retrieves the document data and passes it to the next step for transformation or storage.
Send (POST, PUT, DELETE)
Use Send to transmit data to an external HTTP service.
-
POST – Sends data to create a new resource.
-
PUT – Updates an existing resource.
-
DELETE – Removes a resource.
Example Use Case
Send a new order record to the TP API:
| Field | Example |
|---|---|
| URL | https://api.tp-company.com/v1/orders |
| Method | POST |
| Headers | Content-Type: application/json |
| Body | Order data mapped from the process document |
The process sends the document payload in the HTTP request body. The TP endpoint validates the credentials, processes the request, and returns a response such as a confirmation ID or status.
Listen (Server Mode)
Use Listen when you want Boomi to receive HTTP requests instead of sending them.
-
The connector runs in server mode and listens for incoming messages.
-
External systems call the runtime’s exposed URL to trigger the process.
-
The process begins when data is received.
Example Use Case
A logistics partner sends shipment updates to your Boomi process.
| Field | Example |
|---|---|
| Listening Path | /api/shipments/update |
| Authentication | Basic (if required) |
| Method | POST |
| Payload Type | JSON |
When the TP system sends a POST request to https://runtime-host/api/shipments/update, the process starts and processes the received data.
Ensure that your runtime is accessible over the network and the firewall allows incoming HTTP requests on the configured port.
Common issues
| Problem | Possible Cause | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
401 Unauthorized | Invalid username or password | Verify credentials and authentication type |
404 Not Found | Incorrect URL or endpoint path | Check endpoint spelling or base path |
| Timeout | Network or firewall restrictions | Ensure runtime can reach the URL |
500 Internal Server Error | Issue at remote API | Contact API owner or retry later |
Best Practices
-
Always use HTTPS for secure data exchange.
-
Avoid hard coding credentials; store them in Environment Extensions.
-
Test the endpoint using Postman or curl before configuring the connector.
-
For Listen mode, confirm that network and firewall settings allow inbound connections.
-
Document URLs and authentication details for all environments.
-
Log responses for troubleshooting and auditing.
