Using CORS rules for RESTish requests
The Platform API and Partner API support the W3C Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) protocol.
Support for the CORS protocol enables the Platform APIs to circumvent a browser’s same-origin policy, thereby enabling you to implement cross-server, JavaScript-powered API requests.
By using Access-Control-... HTTP headers, CORS essentially allows JavaScript from one origin (server) to request permission from another origin (server) to make RESTish API requests.
To enable CORS requests under a account, you must configure CORS request matching rules for the account on the CORS page (Settings > Boomi Platform API > CORS). Each rule specifies:
-
An origin for matching cross-server RESTish API requests under the account. The matching criteria specified for an origin are protocol (HTTP or HTTPS), originating domain, and originating port. A matching request is one that matches on all criteria.
-
The allowed HTTP methods — GET, POST, DELETE — for matched requests.
CORS request types
There are two types of CORS requests — preflight and normal.
Preflight
A preflight request is used by a browser running JavaScript to determine whether they have permission to perform a given action. The browser sends an API request to determine whether the HTTP method for that type of request is accepted under that account from the origin server. Preflight requests must conform with the following requirements: Specify the HTTP OPTIONS method. Include the Specify the HTTP method for the API request as the Preflight requests are not authenticated. Preflight responses may be cached for up to one hour (3,600 seconds), as indicated by the The following is an example of an excerpt from a preflight request: If the target API request is of a type allowed under the requesting account from the origin server, an excerpt from the response would be as follows: If the target API request is not of a type allowed under the requesting account from the origin server, the response status code would be 401 Unauthorized. Preflight requests are not required for cross-origin requests that can be made from a browser without using CORS, such as an HTML form POST.Details
Origin header.Access-Control-Request-Method header value.Access-Control-Max-Age header value in the response.OPTIONS /api/rest/v1/account-123456/Atom/3456789a-bcde-f012-3456-789abcdef012 HTTP/1.1
Origin: https://mydomain.com
Access-Control-Request-Method: DELETE
Access-Control-Request-Headers: accept, authorization, content-typeAccess-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: cache-control,content-type,expires,last-modified,accept,content-language,authorization,pragma
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://mydomain.com
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, DELETE
Access-Control-Max-Age: 3600
Normal
If the response to a preflight request is positive — the specified type of API request from the specified origin is allowed under the requesting account — the browser then submits the normal request. Normal requests consist of: an API request of the type specified as the target in the preflight request the same account and Normal requests require authentication. The following is an example of an excerpt from a normal request: An example of a positive response to the normal request would be as follows: If the specified type of API request from the specified origin is not allowed under the requesting account, the response status code would be 200 and the Details
Origin header specified in the preflight requestDELETE /api/rest/v1/account-123456/Atom/3456789a-bcde-f012-3456-789abcdef012 HTTP/1.1
Origin: https://mydomain.comAccess-Control-Allow-Origin: https://mydomain.com
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: trueAccess-Control-... headers would be omitted.
For information about using CORS to implement cross-server, JavaScript-powered user interaction, see the CORS tutorial at HTML5Rocks.
Implementing CORS rules
Click the Add Origin button on the CORS page to implement your desired rules. 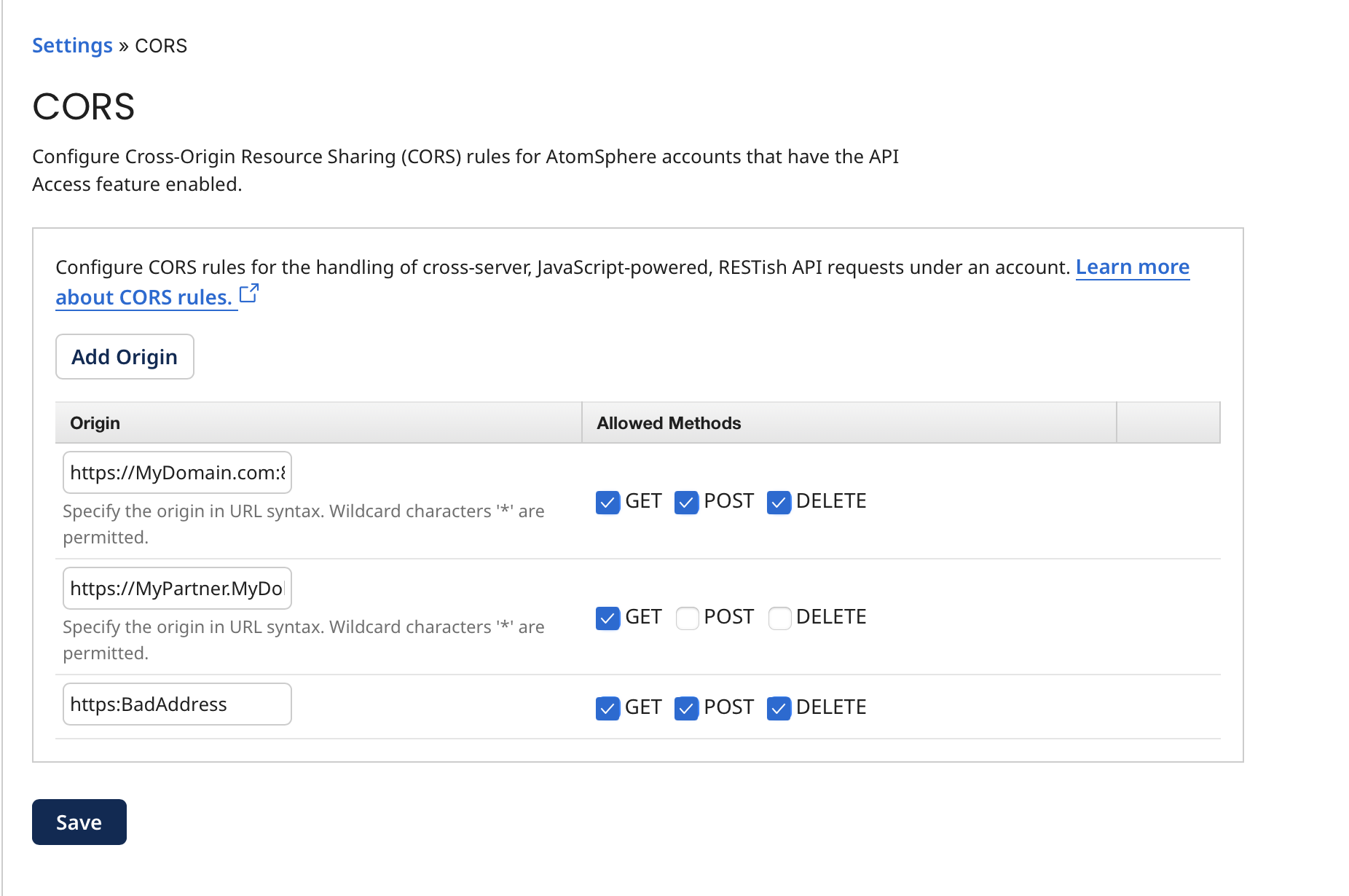
Origin
Specify the origin in URL syntax:
-
Type
://as the delimiter between protocol and domain. -
If you are specifying a port explicitly, type ':' as the delimiter between domain and port. For example:
https://mydomain.com:8081.
The default ports are 80 for HTTP and 443 for HTTPS.
The wildcard character * is permitted in the domain — for example, *.mydomain.com. However, specifying only * (to represent any domain) is not permitted.
Allowed Methods
Sets the allowable HTTP methods for requests from the specified origin.
- GET - If selected, GET requests are allowed.
- POST - If selected, POST requests are allowed.
- DELETE - If selected, DELETE requests are allowed.
Highlight a rule and click the red 'X' icon to delete that rule.
