Exception step
The Exception step provides the ability to terminate the data flow down a path and defines custom error messages to be reported on the Manage menu's Process Reporting page. Exception steps are often used when document data fails to meet certain conditions of a Route or Decision step and should not be processed further.
Custom error messages can be a mix of static and dynamic content. Dynamic content is populated using parameters, which can represent values such as data from a document field, the current system date/time, a static value, the results of a database query, or a number of other values. You can use multiple parameters when creating a message. The placeholder number corresponds to the order of the parameters defined at the bottom of the dialog.
Configuring Exception step
-
On the General tab, in the Display Name field, enter the name to describe the step. If you do not specify the name, “Exception” appears on the step.
-
In the Title field, enter the title name.
The title appears as the subject of the alert message and the initial log message in the process log. -
For the On Failure Behavior field, select one of the following options:
- Continue executing other documents: If selected (recommended for most situations), only the single document that reached the Exception step is marked as failed. Other documents continue to process normally.
- Stop executing the entire process and mark all documents as failed: If selected, the entire process halts immediately, and the process and all documents are marked as failed.
-
In the Message field, enter the message.
The free-flow text message that is generated by the Exception step, and used as the alert message and log details. To specify variables, use the following syntax to create a placeholder, starting at 1:{<parameter number>}.In messages, the single quote (') is a special character. The following points regarding single quotes apply only to the message text that you enter. Single quotes are not stripped if they are coming in as part of the data.
- A single quote by itself is stripped from the message. For example, the message text today's date is rendered as
todays date. - Two consecutive single quotes are rendered as a single quote. For example, the message text today''s date is rendered as
today's date. - An open single quote without a closing single quote escapes the rest of the message. For example, if the variable 1 is the time using a Date Mask of hh, and the variable 2 is the date, an example of the rendering of the message text 1 o'clock 2 would be
12 oclock {2}. - JSON content in messages must be escaped by wrapping it with single quotes, thereby distinguishing it from a variable.
The Date Mask in a variable of type Date and Time cannot have an open single quote without a closing single quote.
- If the Date Mask contains a single quote before some text and a single quote after the text, the single quotes are treated as escape characters. They cause the text between the single quotes to appear in the message. Consider a Date and Time variable using a Date Mask of yyyy.MM.dd G 'at' HH:mm:ss z. An example of the rendering of the variable is
2012.12.18 AD at 15:08:56 PDT(with the wordatappearing in the message). - You can use a combination of single quotes and two consecutive single quotes to get the results you need. Consider a Date and Time variable using a Date Mask of hh 'o''clock' a, zzzz. An example of the rendering of the variable is
1 o'clock PM, Pacific Daylight Time.
- A single quote by itself is stripped from the message. For example, the message text today's date is rendered as
-
For the Variables field, click plus icon to add one or more values to insert into placeholders defined in the message text, Refer to the Parameter values topic for more information.
-
On the Notes tab,
- Enter the title of the note in the Title field.
- Enter the note in the Note field.
-
Click OK to save or click Cancel to cancel configuring the step.
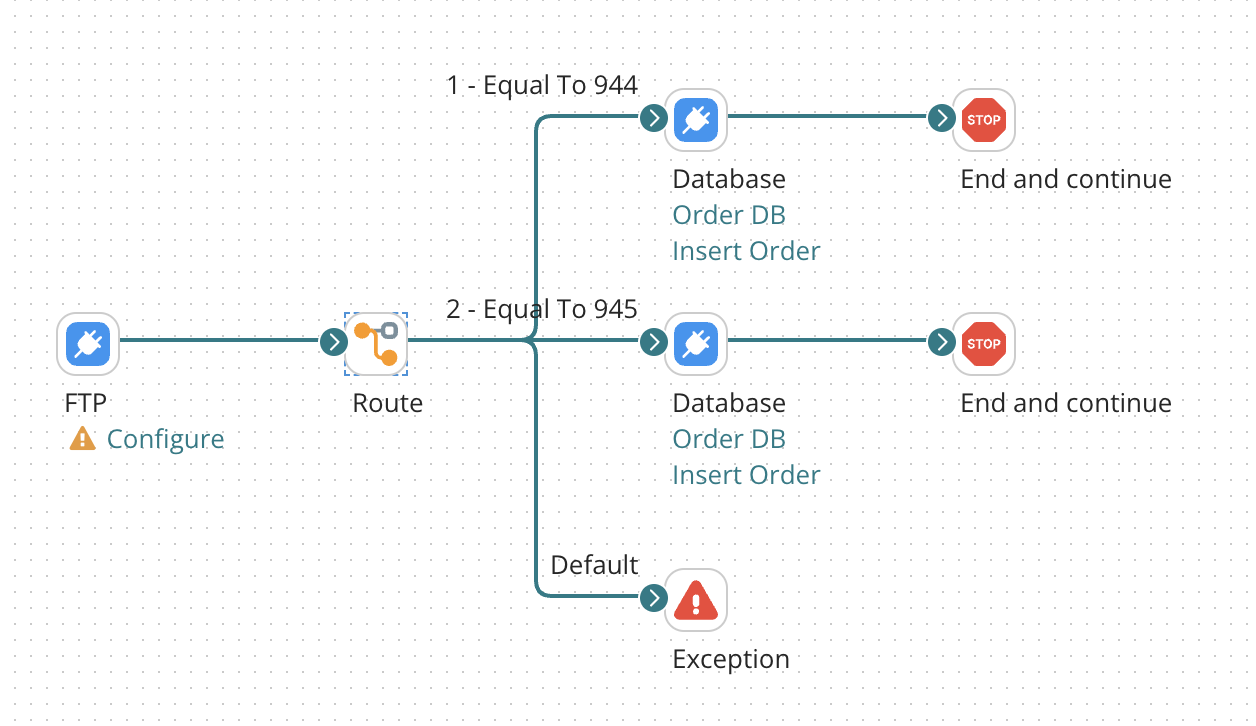
Exception step example
In this scenario, a document is routed according to a specified element in a flat file profile. If the inbound document does not meet the requirement set in the Route step then the document can be routed to an Exception step with an error message.
For example, the Route step checks for inbound 944 and 945 documents. A 940 document comes in. The 940 document will be directed to the Exception step with the following error message: "The document does not meet the requirements set in the Route step. Please review the inbound data." This can help you to troubleshoot an issue because the error is captured in the Exception step with a very specific error message.