Shopify walkthrough
Shopify API version 2024-10 is currently supported.
Integrating Shopify with Data Integration centralizes and automates e-commerce data, enhancing reporting and analytics. You can consolidate sales, customer and product data, streamline data processes, and gain insights to optimize strategies and drive growth.
Connection
To connect Shopify with your destination, refer Shopify connection. Choose a Source connection after creating a connection.
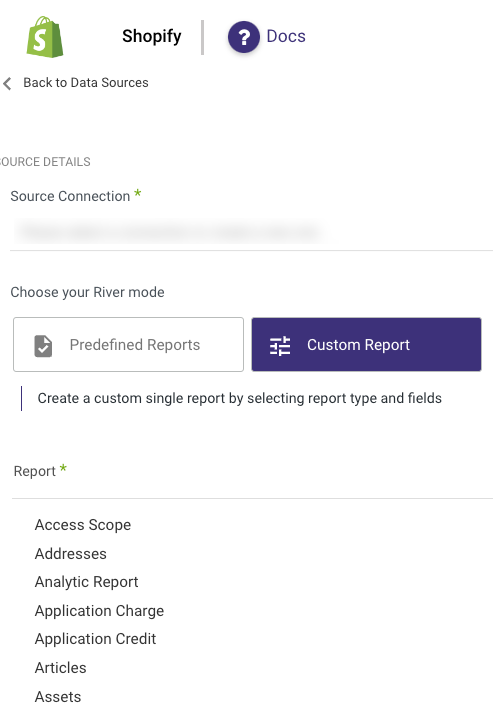
Predefined reports
Data Integration provides a convenient entry point and recommended approach for accessing a range of predefined reports. Each report includes a concise data description, a list of customizable fields (if applicable), and the schema mapping.
Since these reports follow a standardized format, specific fields are locked and can only be accessed through Custom Reports.
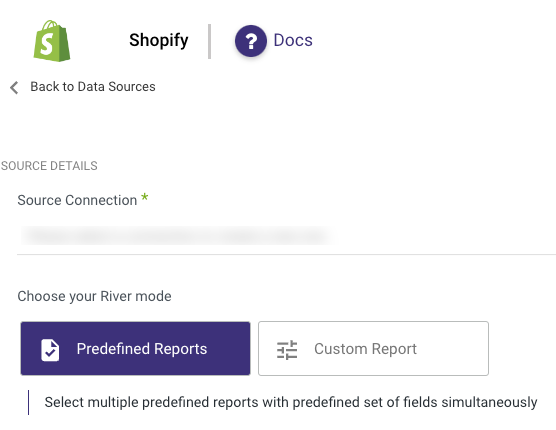
Custom reports
Create custom reports, and select a specific report to pull data from Shopify after establishing a connection.
The following section provides an overview and the API endpoints for the various custom reports:
- Access Scope
- Addresses
- Application Charge
- Application Credit
- Articles
- Assets
- Assigned Fulfillment Order
- Balance
- Blogs
- Carrier Service
- Checkouts
- Collection Listing
- Collection Product
- Collects
- Currencies
- Current User -
GET 'https://[Username].myshopify.com/admin/api/2024-10/users/current.json' - Custom Collection
- Customer Saved Search -
GET 'https://[Username].myshopify.com/admin/api/2024-10/customer_saved_searches.json' - Customers
- Discount Code
- Disputes
- Draft Order
- Events
- Fulfillment Order
- Fulfillment Service -
GET 'https://[Username].myshopify.com/admin/api/2024-10/fulfillment_services.json' - Gift Card
- Inventory Item
- Inventory Level
- Location
- Marketing Event
- Metafields
- Order Transaction
- Orders
- Pages
- Payouts
- Policies
- Price Rule
- Product Image
- Product Metafields
- Products
- Recurring Application Charge
- Redirects
- Refunds
- Resource feedback
- Risks
- Script Tag
- Shop
- Smart Collection
- Storefront Access Token
- Usage Charge
- Users
- Variants
- Webhooks
- Blog Metafields
- Smart Collection Metafields
- Customer Metafields
- Draft Orders Metafields
- Locations Metafields
- Pages Metafields
- Shop Metafields
- Orders Metafields
- Articles Metafields
Access Requirements for Location Report
The Location report requires the read_locations access scope permission.
In Shopify, the Incremental field lets you control your reports based on start date field using one of the two options.
- Updated at - to obtain updated reports.
- Created at - to obtain created reports.
- Start Date is mandatory.
- Data can be retrieved for the date range specified between the start and end dates.
- If you leave the end date blank, the data is pulled at the current time of the river's run.
- Dates timezone : UTC time.
- Use the Last Days Back For Each Run option to gather data from a specified number of days before the selected start date.
- The Start Date does not advance if a River run is unsuccessful.
If you do not want this default setting, click More Options and select the checkbox to advance the start date even if the River run is unsuccessful (Not recommended).

When the data you are fetching is large and you are reaching size or timeout constraints, Split your chunks by to split the data by chunks.
In Shopify, there are 2 input for the Incremental field:
- Time-dependent reports with an incremental field, specify according to which temporal-field the report will be taken from.
- Time-dependent reports without an incremental field indicates that there is only one temporal-field the report can be taken from.
- Additionally, for some of the reports, there are input fields that manage the type of information extracted in those reports, such as, in shop currency in refunds where the currency can be taken according to your shop's currency in Shopify.
Remember to grant read access to all reports you intend to pull. You can configure these permissions in the app's settings under ADMIN API PERMISSION.
Time-dependent reports with or without the incremental field
The 2 types of time-dependent reports are differentiated in steps 1 and 2. Later, step 3 addresses both reports.
- The time-dependent reports with an incremental field include Customers, Orders, Refunds, and more. Select an incremental field for which the report will be chronologically organized, for example, updated at.
- The time-dependent reports without an incremental field include Checkouts, Payout-transactions, etc. Some reports may differ in temporal resolution as follows:
- One option of input depending on the report where the years, months, and days are available,
- While the second option of input where the years, month, days, hours, minutes and seconds with UTC are available.
- All time-dependent reports follow the time input according to a time period. Time-dependent reports support two types of time-period:
-
Date Range
- Pulls data in the date range between the start and end date provided, including the end date.
- You must select a start date.
- Leaving the end date empty will pull data according to the current time of the river's run.
- Select a timezone offset to send dates considering the offset.
- Use the "Last Days Back For Each Run" to expend the start date and pull data a given number of days back before the chosen start date.
-
Predefined date - A date range defined by Data Integration:
- Day - Yesterday.
- Week (From Monday to Sunday) - Week to date, Previous week, Previous week to date.
- Month - Month to date, Previous month, Previous month to date.
- Year - Year to date.
-
Time-independent reports
These reports have no temporal input but may have additional input specified in *.
API limitations
The API uses a leaky bucket protocol where a user may have 40 or 80 maximum available calls and a restoring call rate of 4 calls/sec on the user level.
The Products and Variants reports have an additional throttle that takes effect once a shop has a limit of 50,000 variants. After this threshold is reached, no more than 1,000 new variants can be created per day.
Known issue
In case you see a discrepancy between a number of orders for a given time between Shopify's UI and Data Integration, go over the following steps to make sure you are not missing on the different attributes each platform handles:
-
In case you think you have missing data records, verify that you use the exact same filters and input between each platform. E.g., if you use a week interval, and look on the same set of fields to compare. It is often best to start small and compare a day, and then move forward to summing larger datasets.
-
If you still see a discrepancy, make sure the orders you see in Shopify comes from a single shop. Shopify can combine all orders from different shops, whereas Data Integration pulls orders specific to each shop (which is defined in your connection in Data Integration).
-
If you still see a discrepancy, make sure to differentiate between fields which looks the same. For example, if you compare the number of orders for a specific order id;
id 123456, make sure to compare the order_number field value and not the number field.
Here is an example of data pulled from orders report with a subset from the response:
{'order_number': 200, 'number': 150, 'id': 123456, 'name': '#200'}
If you compared the number field value, you may have assumed to have a discrepancy of 50 orders where in fact they come from the order_number field value.
- When migrating data (or when you want to pull all records), we would suggest using the created_at field as a filter, as opposed to using updated_at field. This is because records in Shopfiy may still be updated while running, causing duplicate records. If you do want to use updated_at, we would suggest using it up until a day or two before the current day to avoid duplicates. You'll still want to review the most recent dates to ensure that duplicates do not exist.
