Logic step types
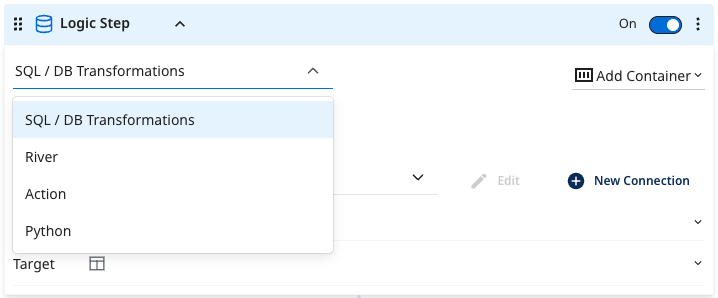
Logic steps are the building blocks of a Logic River, defining specific tasks within it. Select the task type via the Logic Step type drop-down menu in the upper‑left corner of each step.
- SQL / DB Transformation: Run an in-database query or a custom SQL script using the syntax compatible with your cloud database, and then save the results into a table, file, DataFrame, or variable.
- River: Trigger the existing River within your account. This could be a Source to Target River that you wish to coordinate alongside other Source to Target Rivers and transformation steps.
- Action: Make any custom REST call.
- Python: Use Python for easy data manipulation.
Step configuration and requirements
All required fields must be populated to save a Logic River step, including those within disabled steps. You cannot toggle off (disable) a step to bypass validation requirements.
Existing Rivers with missing required fields continue to run without interruption. However, to save updates to these Rivers, you must populate all missing required fields (even in disabled steps).
Required inputs by step type
| Step type | Required fields |
|---|---|
| River | Select a River to run |
| Action | Select an Action to execute |
| SQL / DB – Source | • Connection • Source type (Table, Query, or Dataframe) • SQL Query (Required unless Source type is Dataframe) • Dataframe name (Required if Source type is Dataframe) |
| SQL / DB – Target | Selection: Must choose one Target type (Table, Variable, Dataframe, or File Export) • Target Table (Generic SQL): Table name • Target Table (BigQuery): Dataset name • Target Table (Redshift / Azure / Postgres): Schema name • Target Table (Snowflake): Schema name and Database name • Target Table (Databricks): Database name • Target Variable: Variable name • Target Files Export: FileZone connection • Target DataFrame: Dataframe name and connection |
SQL/DB transformations
The SQL/Script step enables you to perform data transformations using cloud database resources. You can run in-database transformations using a query or SQL statement. Use the SQL syntax supported by the cloud data warehouse. You can customize queries to cleanse, prep, or blend data.
Supported cloud databases include:
- Google BigQuery
- Amazon Redshift
- Snowflake, Databricks
- Azure Synapse Analytics
- Amazon RDS/Aurora for PostgreSQL
- Azure SQL.
Procedure
- Navigate to the Data Integration Console.
- Click the River tab from the left-hand menu.
- Click ADD River and choose Logic River or the existing one from the list.
- Select your desired cloud database and set the connection.
- Enter your query into the SQL box. Click the magnifying glass to enlarge the space to view the query.
- For efficient debugging, build and test your query in your cloud database's query editor.
- If comments are needed, use the syntax /* comment */ syntax. Avoid using the alternate syntax (--comment), as it treats all subsequent lines as comments.
- After pasting the query into the Source section, choose the desired target. In SQL / Script Logic Step types, Data Integration can store the results of the source query into a database table, variable, or file storage.
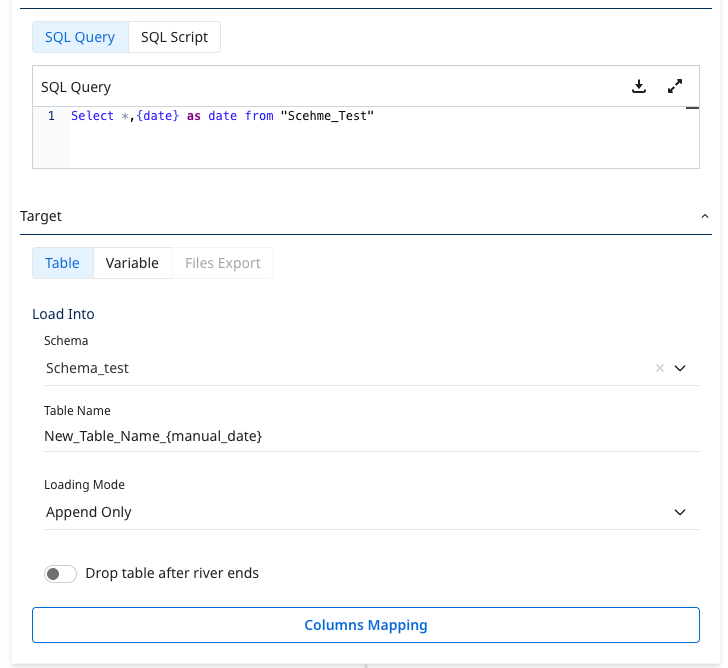
- When storing data into a database table, you can choose between three loading modes:
- Overwrite: Replace the target table with the data from this run. If the target table does not exist, the system creates it.
- Upsert-Merge: Add new or changed records to the target table based on a key defined in the Column Mapping.
- Append Only: Combine the data from this load onto the existing target table.
If you choose Upsert-Merge, you can define your merge key by clicking Column Mapping and highlighting the key indicator for the desired field. You must select Auto Mapping to fetch your table schema.
- Click File export to store data in a target. The file storage type allowed depends on your cloud connection. The supported file store options are Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Azure Blob Storage.
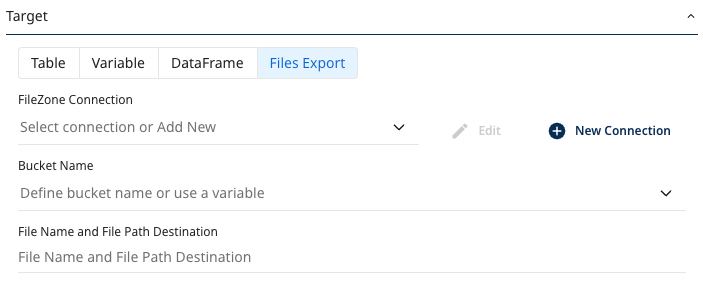
Enter the bucket to save the results and the desired file name. You can customize by file type, delimiter (for CSV), and compression.
- The SQL / Script logic step type can store data values into variables called downstream in the Logic River.
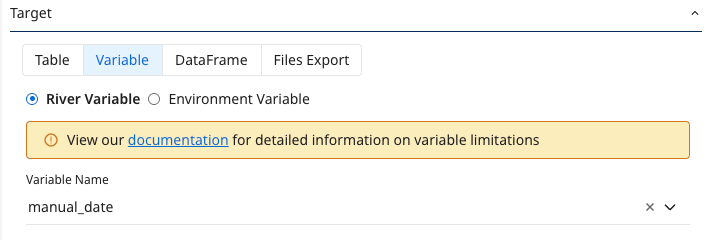
- In a SQL/Script logic step, variables can be stored at the River level or the Environment level.
- River variable lets you pass a dynamic value between steps within the same River session.
- Environment variable is an account-level variable, accessible via the 'Variables' page, and used across multiple Rivers.
River
The River option of a logic step triggers the selected River to run.
For example, the logic step triggers an existing river in our account called 'FB ads', which pulls ad data from the Facebook Ads connector.
Action
The Action logic step triggers an existing Action river in your Data Integration account. Action Rivers lets you make custom REST calls to any API on the web.
Once you select the desired Action River, any inputs corresponding to the River appear for enhanced customization.
For more information on the Action Steps in Logic Rivers, refer to the Action Step.
Python
This feature is a part of the Logic River type. It lets you build a data transformation process using steps, variables, containers, conditions, loops, actions, and River runs. To learn more, refer to the Python Logic Step.
Condition
The Condition logic step provides enhanced conditional capabilities in a Logic River.
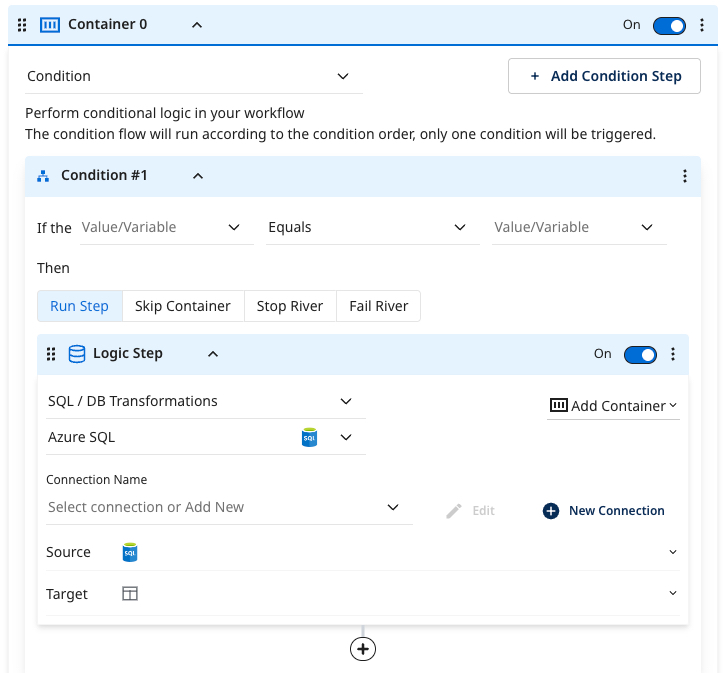
- Enter a static value or an existing variable that meets your condition. Depending on the results of the condition as it is processed, you can decide to execute a step, skip it, halt the process, or terminate the River.
- If the condition is not met, you can use a second conditional container to handle the ELSE scenario for your condition.
