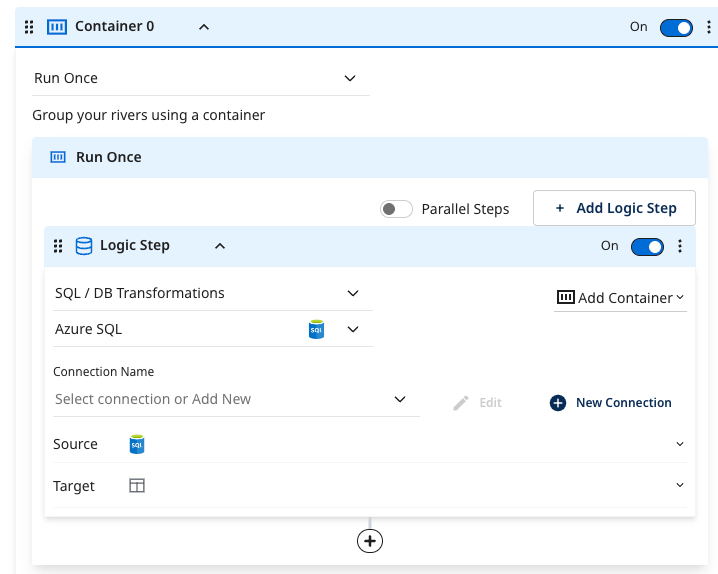
Using logic container
Logic containers enable you to organize your rivers by grouping them into containers. This helps structure your logic and manage multiple steps efficiently.
- Group your rivers using containers by clicking Container Me in any logic step. This wraps the chosen step in a grey container.
- Drag and drop Logic steps into the container or click Add Logic Step to create a new logic step in the current container.
- Click the Parallel Steps toggle to set your logic steps to run in parallel within a container.
Using Logic container run modes
You can control how steps within the container run by selecting an execution mode.
- Run Once: Runs all logic steps inside the container one time.
- Loop Over: Repeats the logic for each item in a defined river list (such as dates, accounts, or regions).
- Condition: Runs logic steps only if a specific condition is met (based on a variable or input).
Run once
The Run Once mode runs all logic steps inside the container once. To update multiple rivers, such as Facebook Ads, Bing Ads, LinkedIn Ads, and X Ads, at once, select this mode. Use this mode for standard one-time operations, such as building or refreshing a reporting table.
Loop over
The Loop Over mode repeats the logic steps inside the container for each item in a specified list (such as dates, accounts, or regions). Use this mode when the same process needs to run for multiple dynamic or parameterized values.

For example, you can use a variable generator like seq4 to create a sequence of monotonically increasing integers. seq4 - wraps integers after reaching the maximum available integer with 4 bytes. This sets up the generator function for the multiple values variable lst.
To use this:
-
Generate the variable to loop. In this example
lst= [[0],[1],[2],[3],..]. i represents each value in the list during each loop iteration. -
Container with the loop over property.
Another instance is pulling a list from the table at the first logic step and loading it into a variable, lst.
Using a loop over for pagination
You can use pagination within logic with a REST action. For example, consider you want to draw IDs from an existing table and put 500 of them in the POST payload each time to fetch their information.
-
Create a list of offset numbers with a 500-incremental jump between them and pass it into payload_offset (payload_offset = [0, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000]). Ensure that the
payload_offsetis set to multiple values. -
Create the payload with each offset (use
order byto ensure the offset does not change the table's original rows). Inside the REST Action river, post a command with the payload{payload}.
Condition
The Condition runs logic steps only if a specific condition is met (based on a variable or input). Use this to control logic flow using flags, user inputs, or system conditions. For example, only run the LinkedIn Ads river if the variable include_linkedin is true.
- Enter a static value or an existing variable that meets your condition. Depending on the results of the condition as it is processed, you can decide to execute a step, skip it, halt the process, or terminate the River.
- If the condition is not met, you can use a second conditional container to handle the ELSE scenario for your condition.
