Variable looping overview
The Variable Looping feature within the REST Action River offers a seamless and efficient iteration method. Rather than iterating over Source to Target Rivers for each endpoint, this lets you loop directly within the Action itself, iterating over a list of parameter values.
This feature provides flexibility in dealing with various scenarios where various parameters need to be processed. For example, when an API endpoint accepts different values for a specific parameter, you can efficiently use Variable Looping to handle all potential cases. This improves load time efficiency and reduces resource consumption.
Configuration overview
You can build a Logic River that fetches animal names from an external API and stores them in a Target data warehouse. Let us use API Ninjas and Data Integration to orchestrate this process through 3 primary steps:
-
Step 1: Action River - Establish the loop: Create a loop that iterates through the values obtained from the API response. Make secondary API calls inside the loop using each value as a parameter to retrieve the corresponding information.
-
Step 2: Source to Target River - Loading the data into a Target: Retrieve data from the previously created Action River. Then, load the collected information into a data warehouse.
-
Step 3: Logic River - Trigger all Rivers and obtain the desired outcome: Access the API call results and the iterated values within your warehouse.
In this step, you can:
- Execute a query to extract information from the Target and save it in a variable.
- Employ the loop created in an Action River to iterate over the variable containing all relevant information.
Procedure
The process includes three primary steps. It is crucial to follow each detail, as several subsequent actions depend on completing them to ensure everything functions properly.
Step 1: Establish the loop (Action river)
- Create an Action River by clicking Create River>Build Your Own. Specify the desired GET call, and insert the API URL.
- Create two variables - one for the iteration process and another to store the values during each iteration.
Make sure to mark the variable that stores the values as Is Private.
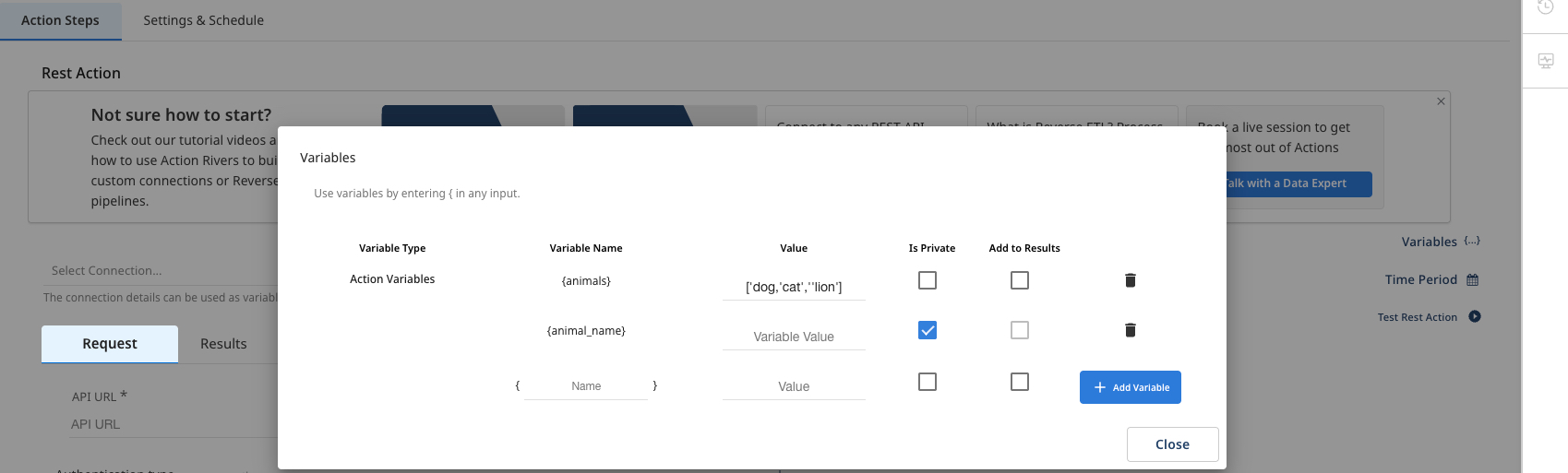
- Add the parameter that corresponds to the previously created iterated variable.
When you click Add under REST URL Params, the specified parameter is automatically appended to the URL.
This process is not visible to the user, and the parameter is added to the URL in the following format: https://api.api-ninjas.com/v1/animals?name={animal_name}
-
Proceed with the authentication of your GET request according to your API.
-
Navigate to the Result tab, and make sure to set Data.
-
Scroll down and expand the Advanced Options.
-
Turn on the Loop Over Variables Values option to true.
-
Enter the variable you created earlier, which you want to iterate over, and specify where to store the values extracted during the iteration process.
-
Enter an Action River name and click Save.
Step 2: Loading the data into a target (Source to Target river)
-
Create a Source to Target River using REST as the Source.
-
Select the one you created from the Action Rivers list.
- Create a Source to Target variable.
Ensure this variable's initial value is populated in square brackets with single quotes, which is necessary for the mapping process to function correctly.
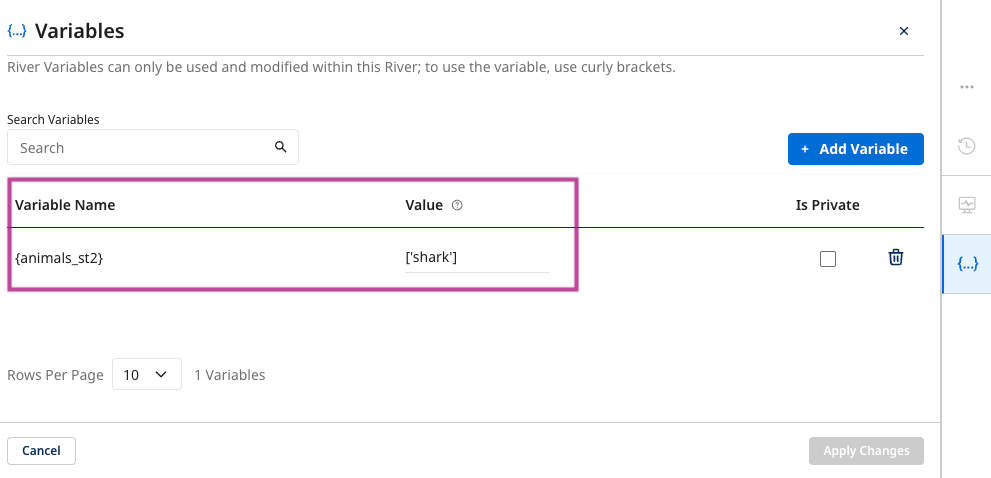
- Enter the variable as the value for the iterated variable from the Action River.
-
Specify your desired Target for the mapping.
-
Navigate to the Schema tab and click Auto Mapping.
-
Enter an Action variable name and click Save.
Step 3: Trigger all rivers and obtain the desired outcome (Logic river)
- Create a Logic River and execute a query to retrieve data from your target, which is / ;\assigned to a variable.

-
Navigate to the Variables tab, create a variable, and turn on the Contains Multiple Values checkbox to configure the variable to hold multiple values.
-
Include an additional step that initiates the Source to Target river.
-
Take the variable created earlier and assign it to a variable from the Source to Target River for iteration.
Make sure to enclose the variable in curly brackets within the Value field.

- Once completed, you can view the API call's results and the iterated values in your data destination warehouse. To learn about the techniques of using Variables. Variable looping use case.
Limitations
-
Only one parameter: The API URL supports a single parameter for iteration.
-
Add a variable to results: When using variable looping, the variables generated from the variable tab cannot be included in the Results section. Therefore, ensure the Add to Results checkbox remains unchecked.
-
Action Rivers with time periods: If you apply specific time periods within an Action River and use it as a REST as a Source in a Source to Target River, you cannot divide the data load into multiple intervals.
-
Nested arrays: Data Integration looping feature does not support nested arrays. Iteration supports only single-level arrays.
-
Maximum character limit: Each parameter has a maximum character limit of 20,000. Inputs exceeding this limit is truncated and may result in an error.
These limitations are specific to the current configuration and are subject to change or enhancement in future releases.
