API Service REST tab
The API Service REST tab is used to generate and configure the API service’s REST endpoints. Endpoints consist of a resource, which identifies an object, and a route, which specifies an operation performed on the object. Resources have one or more associated routes. If you do not have any REST endpoints defined, you are prompted to create one.
You can generate endpoints from processes by clicking Import an Endpoint in the component and selecting the processes. The default settings for the specified operations are derived from the process’s Web Services Server connector’s Listen action.
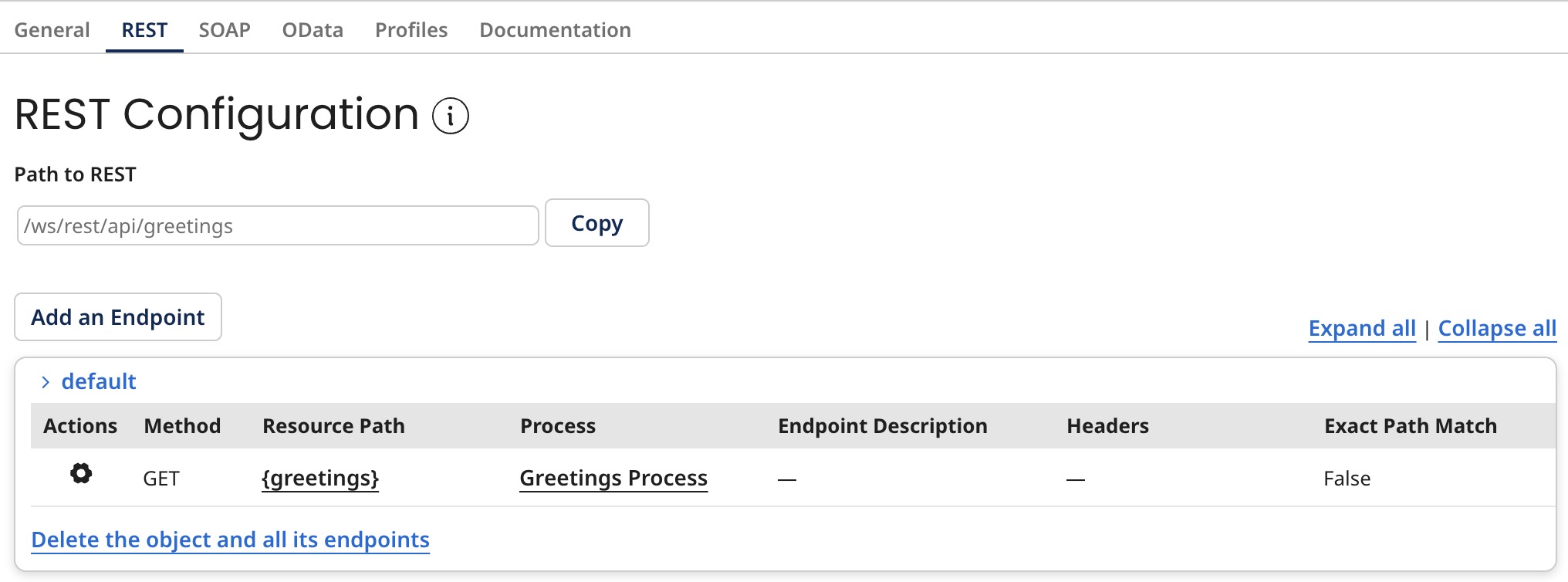
REST endpoints
Resources are listed by object name. Routes are listed by HTTP method, URL path, and HTTP headers, the latter as comma-delineated key-value pairs. If the list entry for a route is truncated due to lack of space, pausing the pointer on the entry displays it in its entirety. Selecting a route enables the controls to the right for configuring the operation specified for the route.
For each item in the list there is an Actions menu:
-
Path to REST
Shows the relative path for the REST endpoints that is pulled into the complete path (along with the Base API Path from the General tab) when the web server is deployed to an runtime. The runtime provides the base URL.
-
Action
Click on the
Actions icon to either edit or delete the endpoint or copy it to SOAP or OData.
-
HTTP Method
Shows the HTTP method used in requests for the operation specified in the route.
- GET — GET or QUERY operation.
- POST — CREATE, EXECUTE or UPSERT operation.
- PUT — UPDATE operation.
- DELETE — DELETE operation.
- PATCH — PATCH operation.
noteThe HTTP method used for an incoming REST request is available to the listener process execution as the dynamic process property
inmethod. -
Resource Path
Shows the resource path for requests for the operation specified in the route. The Resource Path consists of two fields: Object Name and Path Parameters.
-
Object Name
Specified for when requests are made to the specified operation.
-
Path Parameters
Braces {} in the path, for example {id}, delineate the names of parameters. Parameters in the matched part of the path are available to the linked process as dynamic process properties named param_name, where name is the parameter name, for example param_id. The full URL has this form:http://Host:port/REST_url_path/Object/Path_Parameters
where:
Hostandportare set in the Shared Web Server panel (Manage > Runtime Management).REST_url_pathis the Path to REST (this path contains the Base URL specified in the General tab),Object/Path_Parametersis this setting.
For example:
http://machine.domain.tld:9090/ws/rest/Customer/{customerId}
For a set of routes for a given object with HTTP Method GET, the following URL Path usage is typical:
| HTTP Method and URL Path | Usage |
|---|---|
GET / | Return all instances of the object. |
GET /{id} | Return the instance of the object having as its ID the specified id parameter value. |
GET /{id}/metadata | Return metadata for the instance of the object having as its ID the specified id parameter value. |
GET /{id}/{fieldName} | Return the value of the field specified as the fieldName parameter value in the instance of the object having as its ID the specified id parameter value. |
You are not required to set the Resource Path. If you leave the Resource Path empty, the resource path is the default operation from the Base API Path. The Base API Path is set in the Service Configuration section on the General tab of the API Service component.
-
Process
Shows the Web Services Server listener process linked to this endpoint:
-
Clicking the magnifying glass icon opens the component browser for selecting the process.
-
Clicking the edit icon opens the currently selected process for editing.
-
-
Endpoint Description
Description of the REST endpoint.
-
Headers
Shows the defined HTTP headers for requests for the operation. The headers in a request are evaluated for routing purposes in the same manner as static URL path components.
The header name is either a standard HTTP header or a “custom” header.
-
Exact Path Match
Configure endpoints as exact match to ensure they respond only to precisely defined requests. This means the configuration requires static path components to match exactly. Any request must have the same structure as defined in the endpoint configuration. While the system recognizes path variables and captures their values, their positions within the path must also align precisely with the defined structure. However, note that the system respects exact match configurations only if the corresponding process is deployed. If the process is not deployed, the system considers the endpoint undeployed, and its configuration does not apply. When the exact match configuration is unchecked it works on the principle of Best Match where the system finds the most specific or closest matching pattern among deployed endpoints.
